Difference between revisions of "SigL"
(→Reviews) |
(→Original publications) |
||
| Line 155: | Line 155: | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | + | <pubmed>16585774,11274109,1924373 ,16166551 22900538</pubmed> | |
| − | <pubmed>16585774,11274109,1924373 ,16166551 </pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 10:48, 23 July 2014
- Description: sigma factor of the RNA polymerase, Sigma-54, Sigma L
| Gene name | sigL |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | RNA polymerase sigma-54 factor (sigma-L) |
| Function | utilization of arginin, acetoin and fructose, required for cold adaptation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: sigL | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SigL | |
| MW, pI | 49,5 kDa, 7.79 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1308 bp, 436 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | yvfH, yvfG |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 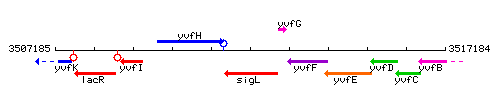
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription, sigma factors and their control
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The SigL regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU34200
Phenotypes of a mutant
The mutant is cold-sensitive and unable to use arginine as a single carbon source. PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU34200
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Binding to promoters of the -12, -24 type
- Protein family: sigma-54 factor family (according to Swiss-Prot) sigma-54 factor family
- Paralogous protein(s):
Transcription factors activating transcription at SigL-dependent promoters
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- DNA binding domain (H-T-H motif) (324–343)
- pron box domain (413–421)
- 3 x Compositional bias domain (6–21),(32–53),(112–136)
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU34200
- Structure:
- UniProt: P24219
- KEGG entry: [3]
Additional information
Transcription initiation by SigL-containing RNA polymerase requires the activity of ATP-hydrolyzing transcription activators.
Transcription factors activating transcription at SigL-dependent promoters
Expression and regulation
- Operon: sigL (according to DBTBS)
- Sigma factor:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Michel Debarbouille, Pasteur Institute, Paris, France Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Bogumiła C Marciniak, Monika Pabijaniak, Anne de Jong, Robert Dűhring, Gerald Seidel, Wolfgang Hillen, Oscar P Kuipers
High- and low-affinity cre boxes for CcpA binding in Bacillus subtilis revealed by genome-wide analysis.
BMC Genomics: 2012, 13;401
[PubMed:22900538]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Frank Wiegeshoff, Carsten L Beckering, Michel Debarbouille, Mohamed A Marahiel
Sigma L is important for cold shock adaptation of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(8);3130-3
[PubMed:16585774]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Soo-Keun Choi, Milton H Saier
Regulation of sigL expression by the catabolite control protein CcpA involves a roadblock mechanism in Bacillus subtilis: potential connection between carbon and nitrogen metabolism.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(19);6856-61
[PubMed:16166551]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N O Ali, J Bignon, G Rapoport, M Debarbouille
Regulation of the acetoin catabolic pathway is controlled by sigma L in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(8);2497-504
[PubMed:11274109]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Débarbouillé, I Martin-Verstraete, F Kunst, G Rapoport
The Bacillus subtilis sigL gene encodes an equivalent of sigma 54 from gram-negative bacteria.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1991, 88(20);9092-6
[PubMed:1924373]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)