Difference between revisions of "ThiO"
(→Extended information on the protein) |
(→Expression and regulation) |
||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
=Expression and regulation= | =Expression and regulation= | ||
| − | * '''Operon:''' | + | * '''Operon:''' ''[[tenA]]-[[tenI]]-[[goxB]]-[[thiS]]-[[thiG]]-[[thiF]]-[[yjbV]]'' {{PubMed|1898926}} |
* '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' | ||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | ||
| − | * '''Additional information:''' | + | * '''Additional information:''' |
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
Revision as of 19:40, 28 September 2009
- Description: FAD-dependent glycine oxidase
| Gene name | thiO |
| Synonyms | goxB, yjbR |
| Essential | no |
| Product | glycine oxidase |
| Function | biosynthesis of thiamine |
| MW, pI | 40 kDa, 5.898 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1107 bp, 369 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | tenI, thiS |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 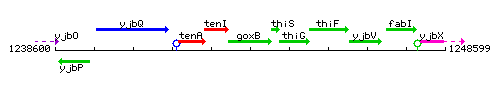
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU11670
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Glycine + H2O + O2 = glyoxylate + NH3 + H2O2 (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: DAMOX/DASOX family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: FAD PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions: the FAD-containing holoenzyme is a homotetramer PubMed
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- UniProt: O31616
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.4.3.19
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Laura Caldinelli, Mattia Pedotti, Laura Motteran, Gianluca Molla, Loredano Pollegioni
FAD binding in glycine oxidase from Bacillus subtilis.
Biochimie: 2009, 91(11-12);1499-508
[PubMed:19751796]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Mattia Pedotti, Sandro Ghisla, Laura Motteran, Gianluca Molla, Loredano Pollegioni
Catalytic and redox properties of glycine oxidase from Bacillus subtilis.
Biochimie: 2009, 91(5);604-12
[PubMed:19254749]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Mario Mörtl, Kay Diederichs, Wolfram Welte, Gianluca Molla, Laura Motteran, Gabriella Andriolo, Mirella S Pilone, Loredano Pollegioni
Structure-function correlation in glycine oxidase from Bacillus subtilis.
J Biol Chem: 2004, 279(28);29718-27
[PubMed:15105420]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Gianluca Molla, Laura Motteran, Viviana Job, Mirella S Pilone, Loredano Pollegioni
Kinetic mechanisms of glycine oxidase from Bacillus subtilis.
Eur J Biochem: 2003, 270(7);1474-82
[PubMed:12654003]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ethan C Settembre, Pieter C Dorrestein, Joo-Heon Park, Amy M Augustine, Tadhg P Begley, Steven E Ealick
Structural and mechanistic studies on ThiO, a glycine oxidase essential for thiamin biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis.
Biochemistry: 2003, 42(10);2971-81
[PubMed:12627963]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Viviana Job, Giorgia Letizia Marcone, Mirella S Pilone, Loredano Pollegioni
Glycine oxidase from Bacillus subtilis. Characterization of a new flavoprotein.
J Biol Chem: 2002, 277(9);6985-93
[PubMed:11744710]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Nishiya, T Imanaka
Purification and characterization of a novel glycine oxidase from Bacillus subtilis.
FEBS Lett: 1998, 438(3);263-6
[PubMed:9827558]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)