RnjA
- Description: RNase J1
| Gene name | rnjA |
| Synonyms | ykqC |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | RNase J1 |
| Function | RNA processing |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: rnjA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: RNase J1 | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: rnjA | |
| MW, pI | 61 kDa, 5.902 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1665 bp, 555 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | adeC, rpoY |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 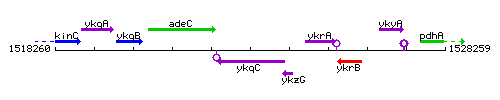
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed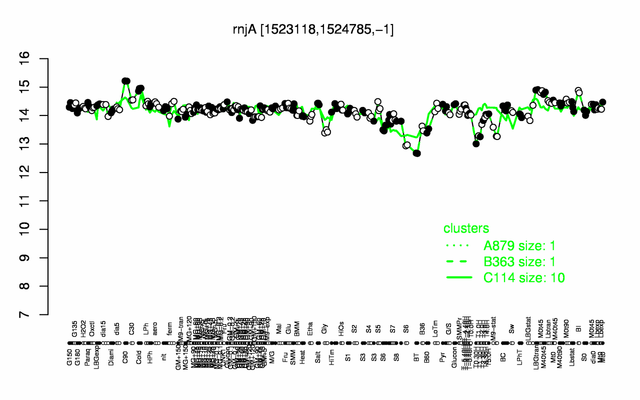
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU14530
Phenotypes of a mutant
- essential PubMed
- a study from the lab of Ciaran Condon reports that rnjA is non-essential and that the mutant is strongly impaired in sporulation, genetic competence and many other phenotypes PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU14530
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: endonuclease and 5'-3' exonuclease
- Protein family: RNase J subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): RnjB
RNAs affected by rnjA
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU14530
- UniProt: Q45493
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- required for thrS RNA processing, involved in maturation of the 5’-end of the16S rRNA
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- translation of YkzG and RnjA is coupled, and this coupling is required for efficient expression of RNase J1 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 2868 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 4928 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 2768 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 4125 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 5056 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP41 (rnjA under control of p(xyl)), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- SSB342 (rnjA under pspac), cat, available in Harald Putzer lab
- Expression vector:
- for chromosomal expression of RNase J1-Strep (spc): GP1034, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- for chromosomal expression of RNase J1-Strep (cat): GP1042, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion: pGP418 (in pAC7), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- FLAG-tag construct:
- GP1020 (spc, based on pGP1331), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP1075 (aphA3), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Harald Putzer, IBPC Paris, France Homepage
David Bechhofer, Mount Sinai School, New York, USA Homepage
Ciaran Condon, IBPC, Paris, France Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Soumaya Laalami, Léna Zig, Harald Putzer
Initiation of mRNA decay in bacteria.
Cell Mol Life Sci: 2014, 71(10);1799-828
[PubMed:24064983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Zbigniew Dominski, Agamemnon J Carpousis, Béatrice Clouet-d'Orval
Emergence of the β-CASP ribonucleases: highly conserved and ubiquitous metallo-enzymes involved in messenger RNA maturation and degradation.
Biochim Biophys Acta: 2013, 1829(6-7);532-51
[PubMed:23403287]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Richard J Lewis, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Stülke
RNA degradation in Bacillus subtilis: an interplay of essential endo- and exoribonucleases.
Mol Microbiol: 2012, 84(6);1005-17
[PubMed:22568516]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
David H Bechhofer
Bacillus subtilis mRNA decay: new parts in the toolkit.
Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA: 2011, 2(3);387-94
[PubMed:21957024]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jamie Richards, Joel G Belasco
Ribonuclease J: how to lead a double life.
Structure: 2011, 19(9);1201-3
[PubMed:21893280]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ciarán Condon, David H Bechhofer
Regulated RNA stability in the Gram positives.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2011, 14(2);148-54
[PubMed:21334965]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ciarán Condon
What is the role of RNase J in mRNA turnover?
RNA Biol: 2010, 7(3);316-21
[PubMed:20458164]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications
Ailar Jamalli, Agnès Hébert, Léna Zig, Harald Putzer
Control of expression of the RNases J1 and J2 in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(2);318-24
[PubMed:24187087]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sabine Figaro, Sylvain Durand, Laetitia Gilet, Nadège Cayet, Martin Sachse, Ciarán Condon
Bacillus subtilis mutants with knockouts of the genes encoding ribonucleases RNase Y and RNase J1 are viable, with major defects in cell morphology, sporulation, and competence.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(10);2340-8
[PubMed:23504012]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sylvain Durand, Laetitia Gilet, Philippe Bessières, Pierre Nicolas, Ciarán Condon
Three essential ribonucleases-RNase Y, J1, and III-control the abundance of a majority of Bacillus subtilis mRNAs.
PLoS Genet: 2012, 8(3);e1002520
[PubMed:22412379]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Joseph A Newman, Lorraine Hewitt, Cecilia Rodrigues, Alexandra S Solovyova, Colin R Harwood, Richard J Lewis
Dissection of the network of interactions that links RNA processing with glycolysis in the Bacillus subtilis degradosome.
J Mol Biol: 2012, 416(1);121-36
[PubMed:22198292]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jamie Richards, Quansheng Liu, Olivier Pellegrini, Helena Celesnik, Shiyi Yao, David H Bechhofer, Ciarán Condon, Joel G Belasco
An RNA pyrophosphohydrolase triggers 5'-exonucleolytic degradation of mRNA in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell: 2011, 43(6);940-9
[PubMed:21925382]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shiyi Yao, Jamie Richards, Joel G Belasco, David H Bechhofer
Decay of a model mRNA in Bacillus subtilis by a combination of RNase J1 5' exonuclease and RNase Y endonuclease activities.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(22);6384-6
[PubMed:21908660]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Audrey Dorléans, Inés Li de la Sierra-Gallay, Jérémie Piton, Léna Zig, Laetitia Gilet, Harald Putzer, Ciarán Condon
Molecular basis for the recognition and cleavage of RNA by the bifunctional 5'-3' exo/endoribonuclease RNase J.
Structure: 2011, 19(9);1252-61
[PubMed:21893286]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Joseph A Newman, Lorraine Hewitt, Cecilia Rodrigues, Alexandra Solovyova, Colin R Harwood, Richard J Lewis
Unusual, dual endo- and exonuclease activity in the degradosome explained by crystal structure analysis of RNase J1.
Structure: 2011, 19(9);1241-51
[PubMed:21893285]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Gintaras Deikus, David H Bechhofer
5' End-independent RNase J1 endonuclease cleavage of Bacillus subtilis model RNA.
J Biol Chem: 2011, 286(40);34932-40
[PubMed:21862575]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Joseph Newman, Fabian M Rothe, Alexandra S Solovyova, Cecilia Rodrigues, Christina Herzberg, Fabian M Commichau, Richard J Lewis, Jörg Stülke
RNase Y in Bacillus subtilis: a Natively disordered protein that is the functional equivalent of RNase E from Escherichia coli.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(19);5431-41
[PubMed:21803996]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Henrike Pförtner, Leonie Rempeters, Nico Pietack, Christina Herzberg, Jörg Stülke
The RNA degradosome in Bacillus subtilis: identification of CshA as the major RNA helicase in the multiprotein complex.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 77(4);958-71
[PubMed:20572937]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shiyi Yao, David H Bechhofer
Initiation of decay of Bacillus subtilis rpsO mRNA by endoribonuclease RNase Y.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(13);3279-86
[PubMed:20418391]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Nathalie Mathy, Agnès Hébert, Peggy Mervelet, Lionel Bénard, Audrey Dorléans, Inés Li de la Sierra-Gallay, Philippe Noirot, Harald Putzer, Ciarán Condon
Bacillus subtilis ribonucleases J1 and J2 form a complex with altered enzyme behaviour.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 75(2);489-98
[PubMed:20025672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yulia Redko, Ciarán Condon
Maturation of 23S rRNA in Bacillus subtilis in the absence of Mini-III.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(1);356-9
[PubMed:19880604]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shiyi Yao, Josh S Sharp, David H Bechhofer
Bacillus subtilis RNase J1 endonuclease and 5' exonuclease activities in the turnover of DeltaermC mRNA.
RNA: 2009, 15(12);2331-9
[PubMed:19850915]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Gintaras Deikus, David H Bechhofer
Bacillus subtilis trp Leader RNA: RNase J1 endonuclease cleavage specificity and PNPase processing.
J Biol Chem: 2009, 284(39);26394-401
[PubMed:19638340]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shiyi Yao, David H Bechhofer
Processing and stability of inducibly expressed rpsO mRNA derivatives in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(18);5680-9
[PubMed:19633085]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ming Fang, Wencke-Maria Zeisberg, Ciaran Condon, Vasily Ogryzko, Antoine Danchin, Undine Mechold
Degradation of nanoRNA is performed by multiple redundant RNases in Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2009, 37(15);5114-25
[PubMed:19553197]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Roula Daou-Chabo, Ciarán Condon
RNase J1 endonuclease activity as a probe of RNA secondary structure.
RNA: 2009, 15(7);1417-25
[PubMed:19458035]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Roula Daou-Chabo, Nathalie Mathy, Lionel Bénard, Ciarán Condon
Ribosomes initiating translation of the hbs mRNA protect it from 5'-to-3' exoribonucleolytic degradation by RNase J1.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 71(6);1538-50
[PubMed:19210617]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Fabian M Rothe, Christina Herzberg, Eva Wagner, Daniel Hellwig, Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Elke Hammer, Uwe Völker, Jörg Stülke
Novel activities of glycolytic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: interactions with essential proteins involved in mRNA processing.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2009, 8(6);1350-60
[PubMed:19193632]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ulrike Mäder, Léna Zig, Julia Kretschmer, Georg Homuth, Harald Putzer
mRNA processing by RNases J1 and J2 affects Bacillus subtilis gene expression on a global scale.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 70(1);183-96
[PubMed:18713320]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Gintaras Deikus, Ciarán Condon, David H Bechhofer
Role of Bacillus subtilis RNase J1 endonuclease and 5'-exonuclease activities in trp leader RNA turnover.
J Biol Chem: 2008, 283(25);17158-67
[PubMed:18445592]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Inés Li de la Sierra-Gallay, Léna Zig, Ailar Jamalli, Harald Putzer
Structural insights into the dual activity of RNase J.
Nat Struct Mol Biol: 2008, 15(2);206-12
[PubMed:18204464]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jennifer A Collins, Irnov Irnov, Stephanie Baker, Wade C Winkler
Mechanism of mRNA destabilization by the glmS ribozyme.
Genes Dev: 2007, 21(24);3356-68
[PubMed:18079181]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulf Gerth, Holger Kock, Ilja Kusters, Stephan Michalik, Robert L Switzer, Michael Hecker
Clp-dependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(1);321-31
[PubMed:17981983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shiyi Yao, Joshua B Blaustein, David H Bechhofer
Processing of Bacillus subtilis small cytoplasmic RNA: evidence for an additional endonuclease cleavage site.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2007, 35(13);4464-73
[PubMed:17576666]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Nathalie Mathy, Lionel Bénard, Olivier Pellegrini, Roula Daou, Tingyi Wen, Ciarán Condon
5'-to-3' exoribonuclease activity in bacteria: role of RNase J1 in rRNA maturation and 5' stability of mRNA.
Cell: 2007, 129(4);681-92
[PubMed:17512403]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Robert A Britton, Tingyi Wen, Laura Schaefer, Olivier Pellegrini, William C Uicker, Nathalie Mathy, Crystal Tobin, Roula Daou, Jacek Szyk, Ciarán Condon
Maturation of the 5' end of Bacillus subtilis 16S rRNA by the essential ribonuclease YkqC/RNase J1.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 63(1);127-38
[PubMed:17229210]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Alison Hunt, Joy P Rawlins, Helena B Thomaides, Jeff Errington
Functional analysis of 11 putative essential genes in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2006, 152(Pt 10);2895-2907
[PubMed:17005971]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Sergine Even, Olivier Pellegrini, Lena Zig, Valerie Labas, Joelle Vinh, Dominique Bréchemmier-Baey, Harald Putzer
Ribonucleases J1 and J2: two novel endoribonucleases in B.subtilis with functional homology to E.coli RNase E.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2005, 33(7);2141-52
[PubMed:15831787]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)