Nfo
Revision as of 14:20, 17 April 2014 by 134.76.70.252 (talk)
- Description: type IV apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease
| Gene name | nfo |
| Synonyms | yqfS |
| Essential | no |
| Product | type IV apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease |
| Function | repair of oxidative DNA damage in spores |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: nfo | |
| MW, pI | 32 kDa, 5.371 |
| Gene length, protein length | 891 bp, 297 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yqfT, cshB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 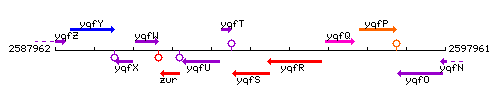
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
DNA repair/ recombination, sporulation proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU25130
Phenotypes of a mutant
- an exoA nfo double mutant is impaired in germination and spore outgrowth due to the accumulation of DNA lesions, this can be rescued by inactivation of disA PubMed
- an exoA nfo double mutant is sensitive to radiation PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU25130
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
- Nfo is functionally redundant with ExoA
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Endonucleolytic cleavage to 5'-phosphooligonucleotide end-products (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: AP endonuclease 2 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU25130
- Structure:
- UniProt: P54476
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
The gene yqfT is located between nfo and yqfU, but is transcribed in the opposite direction.
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 262 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 659 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 612 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 355 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 628 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- available in Mario Pedraza-Reyes' lab
- GP899 (nfo::kan) and GP1502 (nfo::cat), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications