McsA
| Gene name | mcsA |
| Synonyms | yacH |
| Essential | no |
| Product | activator of McsB kinase activity |
| Function | control of CtsR activity |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: mcsA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: McsA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Stress | |
| MW, pI | 20 kDa, 6.624 |
| Gene length, protein length | 555 bp, 185 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ctsR, mcsB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA Advanced_DNA |
Genetic context 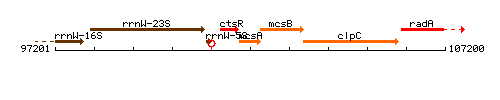
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed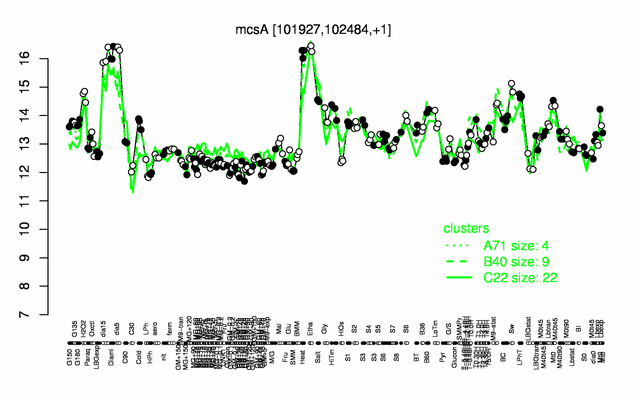
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, sporulation proteins, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB), heat shock proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CtsR regulon, SigB regulon, SigF regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00840
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on Arg-169 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P37569
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: mcsA::aphA3 available from the Gerth lab
- Expression vector: for expression, purification in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, pRSETA available in Gerth lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody: available in Gerth lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Alexander K W Elsholz, Kürsad Turgay, Stephan Michalik, Bernd Hessling, Katrin Gronau, Dan Oertel, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
Global impact of protein arginine phosphorylation on the physiology of Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(19);7451-6
[PubMed:22517742]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jeanette Hahn, Naomi Kramer, Kenneth Briley, David Dubnau
McsA and B mediate the delocalization of competence proteins from the cell poles of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 72(1);202-15
[PubMed:19226326]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Stephanie T Wang, Barbara Setlow, Erin M Conlon, Jessica L Lyon, Daisuke Imamura, Tsutomu Sato, Peter Setlow, Richard Losick, Patrick Eichenberger
The forespore line of gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Biol: 2006, 358(1);16-37
[PubMed:16497325]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Pekka Varmanen, Finn K Vogensen, Karin Hammer, Airi Palva, Hanne Ingmer
ClpE from Lactococcus lactis promotes repression of CtsR-dependent gene expression.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(17);5117-24
[PubMed:12923084]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Petersohn, M Brigulla, S Haas, J D Hoheisel, U Völker, M Hecker
Global analysis of the general stress response of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(19);5617-31
[PubMed:11544224]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Krüger, D Zühlke, E Witt, H Ludwig, M Hecker
Clp-mediated proteolysis in Gram-positive bacteria is autoregulated by the stability of a repressor.
EMBO J: 2001, 20(4);852-63
[PubMed:11179229]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
I Derré, G Rapoport, T Msadek
CtsR, a novel regulator of stress and heat shock response, controls clp and molecular chaperone gene expression in gram-positive bacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 31(1);117-31
[PubMed:9987115]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Krüger, T Msadek, M Hecker
Alternate promoters direct stress-induced transcription of the Bacillus subtilis clpC operon.
Mol Microbiol: 1996, 20(4);713-23
[PubMed:8793870]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)