ClpP
- Description: ATP-dependent Clp protease proteolytic subunit (class III heat-shock protein)
| Gene name | clpP |
| Synonyms | yvdN |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ATP-dependent Clp protease proteolytic subunit |
| Function | protein degradation |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Stress | |
| MW, pI | 21 kDa, 5.008 |
| Gene length, protein length | 591 bp, 197 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | trnQ-Arg, pgcM |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 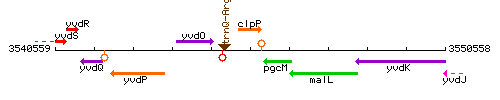
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU34540
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Hydrolysis of proteins to small peptides in the presence of ATP and magnesium (according to Swiss-Prot) endopeptidase/proteolysis
- Protein family: peptidase S14 family (according to Swiss-Prot) ClpP (IPR001907) InterPro, (PF00574) PFAM
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
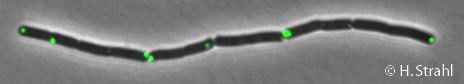
- Localization: cytoplasmic polar clusters, excluded from the nucleoid, induced clustering upon heat shock, colocalization with ClpX, ClpC and ClpE PubMed
Database entries
- Structure: Two homologue structures resolved 1TYF, 1Y7O, structural model of B. subtilis ClpP available from hstrahl
- UniProt: P80244
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 3.4.21.92
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: clpP PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- clpP::spec and clpP::cat available , available in the Leendert Hamoen lab
- GP551 (spc), available in the Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion: C-terminal GFP fusions (both single copy and as 2th copy in amyE locus, also as CFP and YFP variants) available in the Leendert Hamoen lab
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Leendert Hamoen, Newcastle University, UK homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Janine Kirstein, Noël Molière, David A Dougan, Kürşad Turgay
Adapting the machine: adaptor proteins for Hsp100/Clp and AAA+ proteases.
Nat Rev Microbiol: 2009, 7(8);589-99
[PubMed:19609260]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original Publications