RecA
- Description: multifunctional protein involved in homologous recombination and DNA repair (LexA-autocleavage), required to internalize and to recombine ssDNA with homologous resident duplex
| Gene name | recA |
| Synonyms | recE |
| Essential | no |
| Product | multifunctional protein involved in homologous recombination and DNA repair (LexA-autocleavage) |
| Function | DNA repair/ recombination |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: recA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: RecA | |
| MW, pI | 37 kDa, 4.883 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1041 bp, 347 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | cinA, pbpX |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed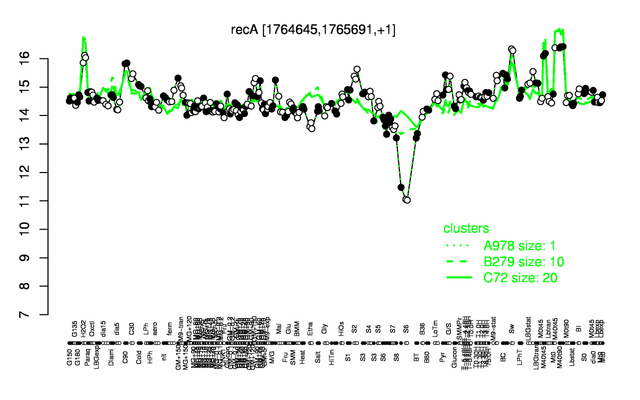
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
DNA repair/ recombination, genetic competence, phosphoproteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16940
Phenotypes of a mutant
- drastically reduced survival of mature dormant spores after exposure to ultrahigh vacuum desiccation and ionizing radiation that induce single strand (ss) DNA nicks and double-strand breaks (DSBs) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16940
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
RecA filaments are dismantled from DNA by PcrA PubMed
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: recA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- colocalizes to the replisome in response to endogenous and exogenous DNA damage and in response to damage-independent fork arrest (formation of DNA repair centers), repair center formation depends on RecO and RecR, and is facilitated by RecF and SsbA PubMed
- Nucleoid (Mid-cell) PubMed
- localizes to one cell pole PubMed
- forms a transient, mobile focus associated with the chromosome during spore development PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16940
- Structure: 1U94 (RecA from E. coli, 62% identity, 86% similarity)
- UniProt: P16971
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: recA PubMed
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 417 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1257 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 5143 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 3169 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 4953 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- IRN444 (cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- 1A746 (recA::erm), PubMed, available at BGSC
- 1A786 (recA::kan), PubMed, available at BGSC
- BP469 (recA::erm), available in Fabian Commichau's lab
- Expression vector: for expression, purification in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, pRSETA available in Ulf Gerth's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Peter Graumann, Freiburg University, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Juan C Alonso, Paula P Cardenas, Humberto Sanchez, James Hejna, Yuki Suzuki, Kunio Takeyasu
Early steps of double-strand break repair in Bacillus subtilis.
DNA Repair (Amst): 2013, 12(3);162-76
[PubMed:23380520]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Dawit Kidane, Silvia Ayora, Joann B Sweasy, Peter L Graumann, Juan C Alonso
The cell pole: the site of cross talk between the DNA uptake and genetic recombination machinery.
Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol: 2012, 47(6);531-55
[PubMed:23046409]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Justin S Lenhart, Jeremy W Schroeder, Brian W Walsh, Lyle A Simmons
DNA repair and genome maintenance in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2012, 76(3);530-64
[PubMed:22933559]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Silvia Ayora, Begoña Carrasco, Paula P Cárdenas, Carolina E César, Cristina Cañas, Tribhuwan Yadav, Chiara Marchisone, Juan C Alonso
Double-strand break repair in bacteria: a view from Bacillus subtilis.
FEMS Microbiol Rev: 2011, 35(6);1055-81
[PubMed:21517913]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Justin Courcelle, Philip C Hanawalt
RecA-dependent recovery of arrested DNA replication forks.
Annu Rev Genet: 2003, 37;611-46
[PubMed:14616075]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Michael M Cox
The bacterial RecA protein as a motor protein.
Annu Rev Microbiol: 2003, 57;551-77
[PubMed:14527291]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Shelley L Lusetti, Michael M Cox
The bacterial RecA protein and the recombinational DNA repair of stalled replication forks.
Annu Rev Biochem: 2002, 71;71-100
[PubMed:12045091]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Cox
Recombinational DNA repair in bacteria and the RecA protein.
Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol: 1999, 63;311-66
[PubMed:10506835]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications
Tribhuwan Yadav, Begoña Carrasco, Ester Serrano, Juan C Alonso
Roles of Bacillus subtilis DprA and SsbA in RecA-mediated genetic recombination.
J Biol Chem: 2014, 289(40);27640-52
[PubMed:25138221]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Justin S Lenhart, Eileen R Brandes, Jeremy W Schroeder, Roderick J Sorenson, Hollis D Showalter, Lyle A Simmons
RecO and RecR are necessary for RecA loading in response to DNA damage and replication fork stress.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(15);2851-60
[PubMed:24891441]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Wojciech W Krajewski, Xin Fu, Martin Wilkinson, Nora B Cronin, Mark S Dillingham, Dale B Wigley
Structural basis for translocation by AddAB helicase-nuclease and its arrest at χ sites.
Nature: 2014, 508(7496);416-9
[PubMed:24670664]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Paula P Cardenas, Carolina Gándara, Juan C Alonso
DNA double strand break end-processing and RecA induce RecN expression levels in Bacillus subtilis.
DNA Repair (Amst): 2014, 14;1-8
[PubMed:24373815]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christian Lesterlin, Graeme Ball, Lothar Schermelleh, David J Sherratt
RecA bundles mediate homology pairing between distant sisters during DNA break repair.
Nature: 2014, 506(7487);249-53
[PubMed:24362571]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ignacija Vlašić, Ramona Mertens, Elena M Seco, Begoña Carrasco, Silvia Ayora, Günther Reitz, Fabian M Commichau, Juan C Alonso, Ralf Moeller
Bacillus subtilis RecA and its accessory factors, RecF, RecO, RecR and RecX, are required for spore resistance to DNA double-strand break.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2014, 42(4);2295-307
[PubMed:24285298]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Tribhuwan Yadav, Begoña Carrasco, James Hejna, Yuki Suzuki, Kunio Takeyasu, Juan C Alonso
Bacillus subtilis DprA recruits RecA onto single-stranded DNA and mediates annealing of complementary strands coated by SsbB and SsbA.
J Biol Chem: 2013, 288(31);22437-50
[PubMed:23779106]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Vladimir Bidnenko, Lei Shi, Ahasanul Kobir, Magali Ventroux, Nathalie Pigeonneau, Céline Henry, Alain Trubuil, Marie-Françoise Noirot-Gros, Ivan Mijakovic
Bacillus subtilis serine/threonine protein kinase YabT is involved in spore development via phosphorylation of a bacterial recombinase.
Mol Microbiol: 2013, 88(5);921-35
[PubMed:23634894]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Aimee H Marceau, Douglas A Bernstein, Brian W Walsh, Walker Shapiro, Lyle A Simmons, James L Keck
Protein interactions in genome maintenance as novel antibacterial targets.
PLoS One: 2013, 8(3);e58765
[PubMed:23536821]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Paula P Cárdenas, Begoña Carrasco, Clarisse Defeu Soufo, Carolina E César, Katharina Herr, Miriam Kaufenstein, Peter L Graumann, Juan C Alonso
RecX facilitates homologous recombination by modulating RecA activities.
PLoS Genet: 2012, 8(12);e1003126
[PubMed:23284295]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alexander K W Elsholz, Kürsad Turgay, Stephan Michalik, Bernd Hessling, Katrin Gronau, Dan Oertel, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
Global impact of protein arginine phosphorylation on the physiology of Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(19);7451-6
[PubMed:22517742]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Tribhuwan Yadav, Begoña Carrasco, Angela R Myers, Nicholas P George, James L Keck, Juan C Alonso
Genetic recombination in Bacillus subtilis: a division of labor between two single-strand DNA-binding proteins.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2012, 40(12);5546-59
[PubMed:22373918]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Paula P Cardenas, Thomas Carzaniga, Sandro Zangrossi, Federica Briani, Esther Garcia-Tirado, Gianni Dehò, Juan C Alonso
Polynucleotide phosphorylase exonuclease and polymerase activities on single-stranded DNA ends are modulated by RecN, SsbA and RecA proteins.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2011, 39(21);9250-61
[PubMed:21859751]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Miriam Kaufenstein, Martin van der Laan, Peter L Graumann
The three-layered DNA uptake machinery at the cell pole in competent Bacillus subtilis cells is a stable complex.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(7);1633-42
[PubMed:21278288]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jeehae Park, Sua Myong, Anita Niedziela-Majka, Kyung Suk Lee, Jin Yu, Timothy M Lohman, Taekjip Ha
PcrA helicase dismantles RecA filaments by reeling in DNA in uniform steps.
Cell: 2010, 142(4);544-55
[PubMed:20723756]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boumediene Soufi, Chanchal Kumar, Florian Gnad, Matthias Mann, Ivan Mijakovic, Boris Macek
Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) applied to quantitative proteomics of Bacillus subtilis.
J Proteome Res: 2010, 9(7);3638-46
[PubMed:20509597]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Dawit Kidane, Begoña Carrasco, Candela Manfredi, Katharina Rothmaier, Silvia Ayora, Serkalem Tadesse, Juan C Alonso, Peter L Graumann
Evidence for different pathways during horizontal gene transfer in competent Bacillus subtilis cells.
PLoS Genet: 2009, 5(9);e1000630
[PubMed:19730681]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lyle A Simmons, Alexi I Goranov, Hajime Kobayashi, Bryan W Davies, Daniel S Yuan, Alan D Grossman, Graham C Walker
Comparison of responses to double-strand breaks between Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis reveals different requirements for SOS induction.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(4);1152-61
[PubMed:19060143]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Isabelle Mortier-Barrière, Marion Velten, Pauline Dupaigne, Nicolas Mirouze, Olivier Piétrement, Stephen McGovern, Gwennaele Fichant, Bernard Martin, Philippe Noirot, Eric Le Cam, Patrice Polard, Jean-Pierre Claverys
A key presynaptic role in transformation for a widespread bacterial protein: DprA conveys incoming ssDNA to RecA.
Cell: 2007, 130(5);824-36
[PubMed:17803906]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Naomi Kramer, Jeanette Hahn, David Dubnau
Multiple interactions among the competence proteins of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 65(2);454-64
[PubMed:17630974]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Syam P Anand, Haocheng Zheng, Piero R Bianco, Sanford H Leuba, Saleem A Khan
DNA helicase activity of PcrA is not required for the displacement of RecA protein from DNA or inhibition of RecA-mediated strand exchange.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(12);4502-9
[PubMed:17449621]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Lyle A Simmons, Alan D Grossman, Graham C Walker
Replication is required for the RecA localization response to DNA damage in Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2007, 104(4);1360-5
[PubMed:17229847]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jean-Christophe Meile, Ling Juan Wu, S Dusko Ehrlich, Jeff Errington, Philippe Noirot
Systematic localisation of proteins fused to the green fluorescent protein in Bacillus subtilis: identification of new proteins at the DNA replication factory.
Proteomics: 2006, 6(7);2135-46
[PubMed:16479537]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Nora Au, Elke Kuester-Schoeck, Veena Mandava, Laura E Bothwell, Susan P Canny, Karen Chachu, Sierra A Colavito, Shakierah N Fuller, Eli S Groban, Laura A Hensley, Theresa C O'Brien, Amish Shah, Jessica T Tierney, Louise L Tomm, Thomas M O'Gara, Alexi I Goranov, Alan D Grossman, Charles M Lovett
Genetic composition of the Bacillus subtilis SOS system.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(22);7655-66
[PubMed:16267290]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Dawit Kidane, Peter L Graumann
Dynamic formation of RecA filaments at DNA double strand break repair centers in live cells.
J Cell Biol: 2005, 170(3);357-66
[PubMed:16061691]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Begoña Carrasco, Silvia Ayora, Rudi Lurz, Juan C Alonso
Bacillus subtilis RecU Holliday-junction resolvase modulates RecA activities.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2005, 33(12);3942-52
[PubMed:16024744]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hanne Jarmer, Randy Berka, Steen Knudsen, Hans H Saxild
Transcriptome analysis documents induced competence of Bacillus subtilis during nitrogen limiting conditions.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2002, 206(2);197-200
[PubMed:11814663]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L W Hamoen, B Haijema, J J Bijlsma, G Venema, C M Lovett
The Bacillus subtilis competence transcription factor, ComK, overrides LexA-imposed transcriptional inhibition without physically displacing LexA.
J Biol Chem: 2001, 276(46);42901-7
[PubMed:11555642]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B J Haijema, D van Sinderen, K Winterling, J Kooistra, G Venema, L W Hamoen
Regulated expression of the dinR and recA genes during competence development and SOS induction in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1996, 22(1);75-85
[PubMed:8899710]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C M Lovett, K C Cho, T M O'Gara
Purification of an SOS repressor from Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1993, 175(21);6842-9
[PubMed:8226626]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D L Cheo, K W Bayles, R E Yasbin
Elucidation of regulatory elements that control damage induction and competence induction of the Bacillus subtilis SOS system.
J Bacteriol: 1993, 175(18);5907-15
[PubMed:7690748]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)