SigE
- Description: RNA polymerase sporulation mother cell-specific (early) sigma factor SigE
| Gene name | sigE |
| Synonyms | spoIIGB |
| Essential | no |
| Product | RNA polymerase sporulation mother cell-specific (early) sigma factor SigE |
| Function | transcription of sporulation genes (early mother cell) |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: sigE | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SigE | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: sigE | |
| MW, pI | 27 kDa, 9.212 |
| Gene length, protein length | 717 bp, 239 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | spoIIGA, sigG |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 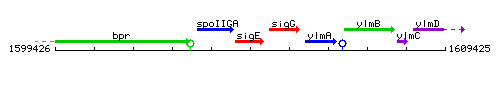
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed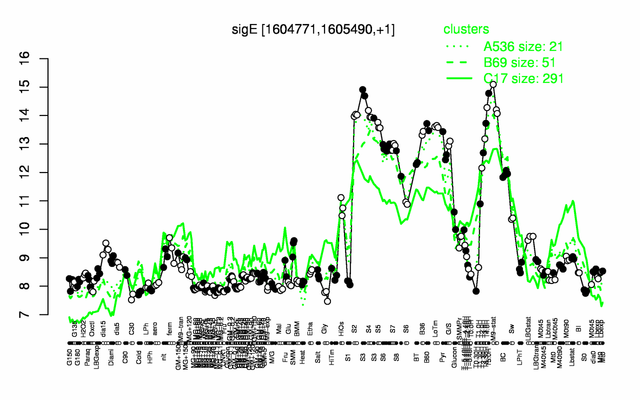
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription, sigma factors and their control, sporulation proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
SinR regulon, Spo0A regulon, Efp-dependent proteins
The SigE regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15320
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU15320
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: RNA polymerase sigma factor, active in the mother cell
- Protein family: sigma-70 factor family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU15320
- Structure:
- UniProt: P06222
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
- translation is likely to require Efp due to the presence of several consecutive proline residues PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
- Bill Haldenwang, San Antonio, USA
- Charles Moran, Emory University, NC, USA homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Michiel J L de Hoon, Patrick Eichenberger, Dennis Vitkup
Hierarchical evolution of the bacterial sporulation network.
Curr Biol: 2010, 20(17);R735-45
[PubMed:20833318]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
The SigE regulon
Original Publications
Additional publications: PubMed