CitB
- Description: aconitate hydratase (aconitase)
| Gene name | citB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | aconitate hydratase (aconitase) |
| Function | TCA cycle |
| MW, pI | 99 kDa, 4.903 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2727 bp, 909 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | sspO, yneN |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 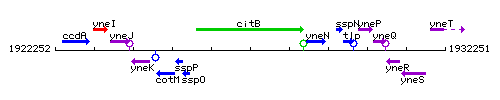
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates:
Phenotypes of a mutant
glutamate auxotrophy and a defect in sporulation PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry:
- KEGG entry:
- E.C. number: 4.2.1.3
Additional information
B. subtilis aconitase is both an enzyme and an RNA binding protein PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Operon: citB
- Sigma factor: SigA
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP683 (erm), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
- Rosenkrantz MS, Dingman DW, Sonenshein AL (1985) Bacillus subtilis citB gene is regulated synergistically by glucose and glutamine. J Bacteriol 164:155-164. PubMed
- Jourlin-Castelli C, Mani N, Nakano MM, Sonenshein AL (2000) CcpC, a novel regulator of the LysR family required for glucose repression of the citB gene in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol 295:865-878. PubMed
- Alén C, Sonenshein AL (1999) Bacillus subtilis aconitase is an RNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10412-10417. PubMed
- Fisher SH, Magasanik B (1984) 2-Ketoglutarate and the regulation of aconitase and histidase formation Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 158:379-382. PubMed
- Kim, H. J., S. I. Kim, M. Ratnayake-Lecamwasam, K. Tachikawa, A. L. Sonenshein, and M. Strauch. (2003) Complex regulation of the Bacillus subtilis aconitase gene. J. Bacteriol. 185:1672-1680. PubMed
- Blencke, H.-M., Reif, I., Commichau, F. M., Detsch, C., Wacker, I., Ludwig, H. & Stülke, J. (2006) Regulation of citB expression in Bacillus subtilis: Integration of multiple metabolic signals in the citrate pool and by the general nitrogen regulatory system. Arch. Microbiol. 185: 136-146. PubMed
- Serio, A. W., Pechter, K. B., and Sonenshein, A. L. (2006) Bacillus subtilis aconitase is required for efficient late-sporulation gene expression. J Bacteriol 188: 6396-6405. PubMed
- Nakano MM, Zuber P, Sonenshein AL (1998) Anaerobic regulation of Bacillus subtilis Krebs cycle genes. J Bacteriol. 180:3304-3311. PubMed
- Craig JE, Ford MJ, Blaydon DC, Sonenshein AL (1997) A null mutation in the Bacillus subtilis aconitase gene causes a block in Spo0A-phosphate-dependent gene expression. J Bacteriol 197:7351-7359. PubMed
- Kim HJ, Kim SI, Ratnayake-Lecamwasam M, Tachikawa K, Sonenshein AL, Strauch M (2003) Complex regulation of the Bacillus subtilis aconitase gene. J Bacteriol. 185:1672-1680. PubMed
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed