Difference between revisions of "YbcT"
(→Expression and regulation) |
|||
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
| − | ** repressed during logrithmic growth ([[AbrB]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/ | + | ** repressed during logrithmic growth ([[AbrB]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/17720793 PubMed] |
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' activated by [[YvrHb]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16306698 PubMed], repressed by [[AbrB]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/19465659 PubMed], activated by [[Abh]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/19465659 PubMed] | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' activated by [[YvrHb]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16306698 PubMed], repressed by [[AbrB]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/19465659 PubMed], activated by [[Abh]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/19465659 PubMed] | ||
** [[AbrB]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15687200,17720793 PubMed] | ** [[AbrB]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15687200,17720793 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** [[AbrB]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15687200,17720793 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** [[AbrB]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15687200,17720793 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** [[AbrB]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15687200,17720793 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** [[AbrB]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/17720793 PubMed] | ||
* '''Additional information:''' the mRNA is very stable (half-life > 15 min) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12884008 PubMed] | * '''Additional information:''' the mRNA is very stable (half-life > 15 min) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12884008 PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 12:28, 11 June 2009
- Description: sublancin 168 lantibiotic antimicrobial precursor peptide
| Gene name | sunA |
| Synonyms | yolG |
| Essential | no |
| Product | sublancin 168 lantibiotic antimicrobial precursor peptide |
| Function | antimicrobial peptide |
| MW, pI | 5 kDa, 7.963 |
| Gene length, protein length | 168 bp, 56 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | sunT, sunI |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 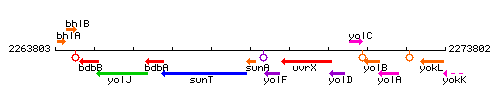
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU21480
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: IPP isomerase type 2 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry: P68577
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: sunA
- Additional information: the mRNA is very stable (half-life > 15 min) PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Yun Luo, John D Helmann
Extracytoplasmic function sigma factors with overlapping promoter specificity regulate sublancin production in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(15);4951-8
[PubMed:19465659]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Masakuni Serizawa, Keisuke Kodama, Hiroki Yamamoto, Kazuo Kobayashi, Naotake Ogasawara, Junichi Sekiguchi
Functional analysis of the YvrGHb two-component system of Bacillus subtilis: identification of the regulated genes by DNA microarray and northern blot analyses.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem: 2005, 69(11);2155-69
[PubMed:16306698]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed