Difference between revisions of "Sandbox"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' | + | * '''Description:''' transcriptional regulator of transition state genes <br/><br/> |
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Gene name''' | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Gene name''' | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''abrB'' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Synonyms''' || '' '' | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Synonyms''' || ''cpsX '' |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || transcriptional regulator |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || regulation of gene expression during the transition <br/>from growth to stationary phase |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 10 kDa, 6.57 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || 288 bp, 96 aa |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[ | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[yabC]]'', ''[[metS]]'' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Get the DNA and protein [http://srs.ebi.ac.uk/srsbin/cgi-bin/wgetz?-e+[EMBLCDS: | + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Get the DNA and protein [http://srs.ebi.ac.uk/srsbin/cgi-bin/wgetz?-e+[EMBLCDS:CAB11813]+-newId sequences] <br/> (Barbe ''et al.'', 2009)''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image: | + | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:abrB_context.gif]] |
<div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | <div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
=== Basic information === | === Basic information === | ||
| − | * '''Locus tag:''' | + | * '''Locus tag:''' BSU00370 |
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
| + | |||
| + | No swarming motility on B medium. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/19202088 PubMed] | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/ | + | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/abrB.html] |
| − | * '''SubtiList entry:''' [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/genome.cgi?gene_detail+ | + | * '''SubtiList entry:''' [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/genome.cgi?gene_detail+BG10100] |
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| Line 56: | Line 58: | ||
* '''Protein family:''' | * '''Protein family:''' | ||
| − | * '''Paralogous protein(s):''' | + | * '''Paralogous protein(s):''' [[Abh]], [[SpoVT]] (only N-terminal domain) |
| + | |||
| + | === Genes/ operons controlled by AbrB === | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Activated by AbrB:''' ''[[citB]]'', ''[[comK]], [[hpr]]'', ''[[rbsR]]-[[rbsK]]-[[rbsD]]-[[rbsA]]-[[rbsC]]-[[rbsB]]'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * ''' Repressed by AbrB:''' ''[[abrB]], [[aprE]], [[ftsA]]-[[ftsZ]], [[kinC]], [[motA]], [[nprE]], [[pbpE]], [[spo0H]], [[spoVG]], [[spo0E]], [[tycA]], [[sbo]]-[[alb]], [[yqxM]]-[[sipW]]-[[tasA]]'' | ||
=== Extended information on the protein === | === Extended information on the protein === | ||
| Line 68: | Line 76: | ||
* '''Cofactor(s):''' | * '''Cofactor(s):''' | ||
| − | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | + | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' interaction with [[AbbA]] results in inactivation of AbrB [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/18840696 PubMed] |
| − | * '''Interactions:''' | + | * '''Interactions:''' [[AbrB]]-[[AbbA]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/18840696 PubMed] |
* '''Localization:''' | * '''Localization:''' | ||
| Line 76: | Line 84: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''Structure:''' | + | * '''Structure:''' [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1Z0R 1Z0R] (N-terminal DNA recognition domain), 1Z0R (N-terminal DNA recognition domain) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/mmdb/mmdbsrv.cgi?Dopt=s&uid=32611 NCBI] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16223496 PubMed] |
| − | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/ | + | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P08874 P08874] |
| − | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu+ | + | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu+BSU00370] |
| − | + | === Additional information=== | |
| − | |||
=Expression and regulation= | =Expression and regulation= | ||
| − | * '''Operon:''' ''[ | + | * '''Operon:''' ''abrB'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/3145384 PubMed] |
| − | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' [[SigA]] | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' [[SigA]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/3145384 PubMed] |
| − | * '''Regulation:''' repressed during logrithmic growth ([[AbrB]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/ | + | * '''Regulation:''' repressed during logrithmic growth ([[AbrB]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/2504584 PubMed] expressed at the onset of stationary phase [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/3145384 PubMed] |
| − | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' [[AbrB]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/ | + | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' [[AbrB]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/2504584 PubMed] repressed by [[Spo0A]]-P [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/3145384 PubMed] |
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
| Line 100: | Line 107: | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | * '''Mutant:''' | + | * '''Mutant:''' TT731 (aphA3) |
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
| Line 113: | Line 120: | ||
=Labs working on this gene/protein= | =Labs working on this gene/protein= | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Richard Losick]], Harvard Univ., Cambridge, USA [http://www.mcb.harvard.edu/Losick/ homepage] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Mark Strauch]], Baltimore, USA [http://lifesciences.umaryland.edu/Pages/faculty_profile.aspx?ID=212 homepage] | ||
=Your additional remarks= | =Your additional remarks= | ||
| Line 118: | Line 129: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| + | <pubmed>18840696 3145384 8821944 8576231 11101897 11395475 11583849 11964117 11751836 12123659 12076816 12591885 15610005 16223496 16159768 16702211 17660417 17720793 19202088 7592460, 19465659 </pubmed> | ||
| + | # Banse et al. (2008) Parallel pathways of repression and antirepression governing the transition to stationary phase in ''Bacillus subtilis''.''Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA'' '''105:''' 15547-15552. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/18840696 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Perego et al. (1988) Structure of the gene for the transition state regulator, ''abrB'': regulator synthesis is controlled by the ''spo0A'' sporulation gene in ''Bacillus subtilis''. ''Mol. Microbiol.'' '''2:''' 689-699. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/3145384 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Xu, K. and M.A. Strauch. (1996) In vitro selection of optimal AbrB-binding sites: comparison to known in vivo sites indicates flexibility in AbrB-binding and recognition of three-dimensional DNA structures. Molec. Microbiol. 19: 145-158 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8821944 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Xu, K., D. Clark and M.A. Strauch. (1996) Analysis of abrB mutations, mutant proteins, and why abrB does not utilize a perfect consensus in the –35 region of its sigmaA promoter.J. Biol. Chem. 271:2621-2626 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8576231 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Vaughn, J.L., Feher V., Naylor, S., Strauch, M.A. and J. Cavanagh. (2000) Novel DNA binding domain and genetic regulation model of Bacillus subtilis transition state regulator AbrB. Nature Structural Biology 7:1139-1146; [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/11101897 PubMed], Corrigendum appears in Nature Stuctural & Molecular Biology (2005) 12:380 | ||
| + | # Xu, K. and M.A. Strauch. (2001) DNA-binding activity of amino-terminal domains of the Bacillus subtilis AbrB protein. J. Bacteriol. 183:4094-4098 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/11395475 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Phillips, Z. E.V. and M.A. Strauch. (2001) Role of Cys54 in AbrB multimerization and DNA-binding activity. FEMS Microbiol. Letters. 203:207-210 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/11583849 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Phillips, Z.E.V. and M.A. Strauch. (2002) Bacillus subtilis sporulation and stationary phase gene expression. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 59:392-402 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/11964117 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Shafikhani, S.H., Mandic-Mulec, I., Strauch, M.A., Smith, I. and T. Leighton. (2002) Postexponential regulation of sin operon expression in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 184:564-571 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/11751836 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Benson, L. M., Vaughn, J. L., Strauch, M. A., Bobay, B. G., Thompson, R., Naylor, S. and J. Cavanagh (2002). Macromolecular assembly of the transition state regulator AbrB in its unbound and complexed states probed by microelectrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Analytical Biochemistry 306:222-227 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12123659 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Qian, Q., Lee, C.Y., Helmann, J. and M.A. Strauch. (2002) AbrB regulation of the sigmaW regulon of Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol. Letters 211:219-223. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12076816 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Kim, H. J., S. I. Kim, M. Ratnayake-Lecamwasam, K. Tachikawa, A. L. Sonenshein, and M. Strauch. (2003) Complex regulation of the Bacillus subtilis aconitase gene. J. Bacteriol. 185:1672-1680. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12591885 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Bobay, B.G., Benson, L., Naylor, S., Feeney, B., Clark, A.C., Goshe, M.B., Strauch, M.A., Thompson, R., and J.Cavanagh. (2004) Evaluation of the DNA binding tendencies of the transition state regulator AbrB. Biochemistry. 43:16106-16118. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15610005 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Bobay et al.(2005) Revised structure of the AbrB N-terminal domain unifies a diverse superfamily of putative DNA-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 579:5669-5674. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16223496 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Yao, F and M.A. Strauch (2005) Independent and Interchangeable Multimerization Domains of the AbrB, Abh and SpoVT Global Regulatory Proteins. J. Bacteriol. 187:6354-6362 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16159768 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Bobay, B.G., Mueller, G.A., Thompson, R.J., Venters, R.A., Murzin, A.G., Strauch, M.A. & J. Cavanagh (2006) NMR structure of AbhN and comparison with AbrBN: First Insights into the DNA-binding Promiscuity and Specificity of AbrB-like Transition-state Regulator Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 281:21399-21409 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16702211 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Jordan S. Rietkötter E. Strauch MA. Kalamorz F. Butcher BG. Helmann JD. Mascher T. (2007) LiaRS-dependent gene expression is embedded in transition state regulation in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology. 153: 2530-2540. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/17660417 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Strauch MA. Bobay BG. Cavanagh J. Yao F. Wilson A. Le Breton Y. (2007) Abh and AbrB control of Bacillus subtilis antimicrobial gene expression. J. of Bacteriol. 189:7720-7732. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/17720793 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Hamze et al. (2009) Identification of genes required for different stages of dendritic swarming in ''Bacillus subtilis'', with a novel role for ''phrC''. ''Microbiology'' '''155:''' 398-412. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/19202088 PubMed] | ||
| + | # Strauch MA. (1995) AbrB modulates expression and catabolite repression of a Bacillus subtilis ribose transport operon. ''J Bacteriol.'' '''Dec;177(23):'''6727-31. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/7592460 PubMed] | ||
# Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title ''Journal'' '''volume:''' page-page. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | # Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title ''Journal'' '''volume:''' page-page. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 21:11, 10 June 2009
- Description: transcriptional regulator of transition state genes
| Gene name | abrB |
| Synonyms | cpsX |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional regulator |
| Function | regulation of gene expression during the transition from growth to stationary phase |
| MW, pI | 10 kDa, 6.57 |
| Gene length, protein length | 288 bp, 96 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yabC, metS |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 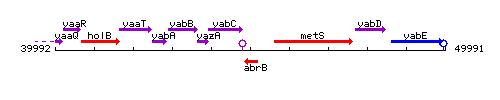
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00370
Phenotypes of a mutant
No swarming motility on B medium. PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
Genes/ operons controlled by AbrB
- Repressed by AbrB: abrB, aprE, ftsA-ftsZ, kinC, motA, nprE, pbpE, spo0H, spoVG, spo0E, tycA, sbo-alb, yqxM-sipW-tasA
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure: 1Z0R (N-terminal DNA recognition domain), 1Z0R (N-terminal DNA recognition domain) NCBI PubMed
- Swiss prot entry: P08874
- KEGG entry: [3]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: abrB PubMed
- Regulation: repressed during logrithmic growth (AbrB) PubMed expressed at the onset of stationary phase PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: TT731 (aphA3)
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Richard Losick, Harvard Univ., Cambridge, USA homepage
Mark Strauch, Baltimore, USA homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Yun Luo, John D Helmann
Extracytoplasmic function sigma factors with overlapping promoter specificity regulate sublancin production in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(15);4951-8
[PubMed:19465659]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kassem Hamze, Daria Julkowska, Sabine Autret, Krzysztof Hinc, Krzysztofa Nagorska, Agnieszka Sekowska, I Barry Holland, Simone J Séror
Identification of genes required for different stages of dendritic swarming in Bacillus subtilis, with a novel role for phrC.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 2);398-412
[PubMed:19202088]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Allison V Banse, Arnaud Chastanet, Lilah Rahn-Lee, Errett C Hobbs, Richard Losick
Parallel pathways of repression and antirepression governing the transition to stationary phase in Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2008, 105(40);15547-52
[PubMed:18840696]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Mark A Strauch, Benjamin G Bobay, John Cavanagh, Fude Yao, Angelo Wilson, Yoann Le Breton
Abh and AbrB control of Bacillus subtilis antimicrobial gene expression.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(21);7720-32
[PubMed:17720793]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Sina Jordan, Eva Rietkötter, Mark A Strauch, Falk Kalamorz, Bronwyn G Butcher, John D Helmann, Thorsten Mascher
LiaRS-dependent gene expression is embedded in transition state regulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2007, 153(Pt 8);2530-2540
[PubMed:17660417]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Benjamin G Bobay, Geoffrey A Mueller, Richele J Thompson, Alexey G Murzin, Ronald A Venters, Mark A Strauch, John Cavanagh
NMR structure of AbhN and comparison with AbrBN: FIRST insights into the DNA binding promiscuity and specificity of AbrB-like transition state regulator proteins.
J Biol Chem: 2006, 281(30);21399-21409
[PubMed:16702211]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Benjamin G Bobay, Antonina Andreeva, Geoffrey A Mueller, John Cavanagh, Alexey G Murzin
Revised structure of the AbrB N-terminal domain unifies a diverse superfamily of putative DNA-binding proteins.
FEBS Lett: 2005, 579(25);5669-74
[PubMed:16223496]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Fude Yao, Mark A Strauch
Independent and interchangeable multimerization domains of the AbrB, Abh, and SpoVT global regulatory proteins.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(18);6354-62
[PubMed:16159768]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Benjamin G Bobay, Linda Benson, Stephen Naylor, Brett Feeney, A Clay Clark, Michael B Goshe, Mark A Strauch, Richele Thompson, John Cavanagh
Evaluation of the DNA binding tendencies of the transition state regulator AbrB.
Biochemistry: 2004, 43(51);16106-18
[PubMed:15610005]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hyun-Jin Kim, Sam-In Kim, Manoja Ratnayake-Lecamwasam, Kiyoshi Tachikawa, Abraham L Sonenshein, Mark Strauch
Complex regulation of the Bacillus subtilis aconitase gene.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(5);1672-80
[PubMed:12591885]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Linda M Benson, Jeffrey L Vaughn, Mark A Strauch, Benjamin G Bobay, Richele Thompson, Stephen Naylor, John Cavanagh
Macromolecular assembly of the transition state regulator AbrB in its unbound and complexed states probed by microelectrospray ionization mass spectrometry.
Anal Biochem: 2002, 306(2);222-7
[PubMed:12123659]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Qiang Qian, Chien Y Lee, John D Helmann, Mark A Strauch
AbrB is a regulator of the sigma(W) regulon in Bacillus subtilis.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2002, 211(2);219-23
[PubMed:12076816]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Z E V Phillips, M A Strauch
Bacillus subtilis sporulation and stationary phase gene expression.
Cell Mol Life Sci: 2002, 59(3);392-402
[PubMed:11964117]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Sasha H Shafikhani, Ines Mandic-Mulec, Mark A Strauch, Issar Smith, Terrance Leighton
Postexponential regulation of sin operon expression in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(2);564-71
[PubMed:11751836]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Z E Phillips, M A Strauch
Role of Cys54 in AbrB multimerization and DNA-binding activity.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2001, 203(2);207-10
[PubMed:11583849]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Xu, M A Strauch
DNA-binding activity of amino-terminal domains of the Bacillus subtilis AbrB protein.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(13);4094-8
[PubMed:11395475]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J L Vaughn, V Feher, S Naylor, M A Strauch, J Cavanagh
Novel DNA binding domain and genetic regulation model of Bacillus subtilis transition state regulator abrB.
Nat Struct Biol: 2000, 7(12);1139-46
[PubMed:11101897]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Xu, D Clark, M A Strauch
Analysis of abrB mutations, mutant proteins, and why abrB does not utilize a perfect consensus in the -35 region of its sigma A promoter.
J Biol Chem: 1996, 271(5);2621-6
[PubMed:8576231]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Xu, M A Strauch
In vitro selection of optimal AbrB-binding sites: comparison to known in vivo sites indicates flexibility in AbrB binding and recognition of three-dimensional DNA structures.
Mol Microbiol: 1996, 19(1);145-58
[PubMed:8821944]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M A Strauch
AbrB modulates expression and catabolite repression of a Bacillus subtilis ribose transport operon.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(23);6727-31
[PubMed:7592460]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Perego, G B Spiegelman, J A Hoch
Structure of the gene for the transition state regulator, abrB: regulator synthesis is controlled by the spo0A sporulation gene in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1988, 2(6);689-99
[PubMed:3145384]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
- Banse et al. (2008) Parallel pathways of repression and antirepression governing the transition to stationary phase in Bacillus subtilis.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105: 15547-15552. PubMed
- Perego et al. (1988) Structure of the gene for the transition state regulator, abrB: regulator synthesis is controlled by the spo0A sporulation gene in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2: 689-699. PubMed
- Xu, K. and M.A. Strauch. (1996) In vitro selection of optimal AbrB-binding sites: comparison to known in vivo sites indicates flexibility in AbrB-binding and recognition of three-dimensional DNA structures. Molec. Microbiol. 19: 145-158 PubMed
- Xu, K., D. Clark and M.A. Strauch. (1996) Analysis of abrB mutations, mutant proteins, and why abrB does not utilize a perfect consensus in the –35 region of its sigmaA promoter.J. Biol. Chem. 271:2621-2626 PubMed
- Vaughn, J.L., Feher V., Naylor, S., Strauch, M.A. and J. Cavanagh. (2000) Novel DNA binding domain and genetic regulation model of Bacillus subtilis transition state regulator AbrB. Nature Structural Biology 7:1139-1146; PubMed, Corrigendum appears in Nature Stuctural & Molecular Biology (2005) 12:380
- Xu, K. and M.A. Strauch. (2001) DNA-binding activity of amino-terminal domains of the Bacillus subtilis AbrB protein. J. Bacteriol. 183:4094-4098 PubMed
- Phillips, Z. E.V. and M.A. Strauch. (2001) Role of Cys54 in AbrB multimerization and DNA-binding activity. FEMS Microbiol. Letters. 203:207-210 PubMed
- Phillips, Z.E.V. and M.A. Strauch. (2002) Bacillus subtilis sporulation and stationary phase gene expression. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 59:392-402 PubMed
- Shafikhani, S.H., Mandic-Mulec, I., Strauch, M.A., Smith, I. and T. Leighton. (2002) Postexponential regulation of sin operon expression in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 184:564-571 PubMed
- Benson, L. M., Vaughn, J. L., Strauch, M. A., Bobay, B. G., Thompson, R., Naylor, S. and J. Cavanagh (2002). Macromolecular assembly of the transition state regulator AbrB in its unbound and complexed states probed by microelectrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Analytical Biochemistry 306:222-227 PubMed
- Qian, Q., Lee, C.Y., Helmann, J. and M.A. Strauch. (2002) AbrB regulation of the sigmaW regulon of Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol. Letters 211:219-223. PubMed
- Kim, H. J., S. I. Kim, M. Ratnayake-Lecamwasam, K. Tachikawa, A. L. Sonenshein, and M. Strauch. (2003) Complex regulation of the Bacillus subtilis aconitase gene. J. Bacteriol. 185:1672-1680. PubMed
- Bobay, B.G., Benson, L., Naylor, S., Feeney, B., Clark, A.C., Goshe, M.B., Strauch, M.A., Thompson, R., and J.Cavanagh. (2004) Evaluation of the DNA binding tendencies of the transition state regulator AbrB. Biochemistry. 43:16106-16118. PubMed
- Bobay et al.(2005) Revised structure of the AbrB N-terminal domain unifies a diverse superfamily of putative DNA-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 579:5669-5674. PubMed
- Yao, F and M.A. Strauch (2005) Independent and Interchangeable Multimerization Domains of the AbrB, Abh and SpoVT Global Regulatory Proteins. J. Bacteriol. 187:6354-6362 PubMed
- Bobay, B.G., Mueller, G.A., Thompson, R.J., Venters, R.A., Murzin, A.G., Strauch, M.A. & J. Cavanagh (2006) NMR structure of AbhN and comparison with AbrBN: First Insights into the DNA-binding Promiscuity and Specificity of AbrB-like Transition-state Regulator Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 281:21399-21409 PubMed
- Jordan S. Rietkötter E. Strauch MA. Kalamorz F. Butcher BG. Helmann JD. Mascher T. (2007) LiaRS-dependent gene expression is embedded in transition state regulation in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology. 153: 2530-2540. PubMed
- Strauch MA. Bobay BG. Cavanagh J. Yao F. Wilson A. Le Breton Y. (2007) Abh and AbrB control of Bacillus subtilis antimicrobial gene expression. J. of Bacteriol. 189:7720-7732. PubMed
- Hamze et al. (2009) Identification of genes required for different stages of dendritic swarming in Bacillus subtilis, with a novel role for phrC. Microbiology 155: 398-412. PubMed
- Strauch MA. (1995) AbrB modulates expression and catabolite repression of a Bacillus subtilis ribose transport operon. J Bacteriol. Dec;177(23):6727-31. PubMed
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed