Difference between revisions of "DisA"
(→Biological materials) |
(→Original publications) |
||
| Line 170: | Line 170: | ||
<pubmed> 22933559 18714086</pubmed> | <pubmed> 22933559 18714086</pubmed> | ||
== Original publications == | == Original publications == | ||
| − | <pubmed>24244006,8793870,9987115,16713562, 23760274,11544224 17434969 18439896 16713555 12493822 21566650 23192352 23608499 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>24244006,8793870,9987115,16713562, 23760274,11544224 17434969 18439896 16713555 12493822 21566650 23192352 23608499 25616256</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 09:25, 28 January 2015
- Description: DNA integrity scanning protein,diadenylate cyclase, delays sporulation in the case of chromosome damage, the DisA-dependent checkpoint arrests DNA replication during B. subtilis spore outgrowth until the germinating spore's genome is free of damage
| Gene name | disA |
| Synonyms | yacK |
| Essential | no |
| Product | DNA integrity scanning protein, has diadenylate cyclase activity |
| Function | control of sporulation initiation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: disA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: DisA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: disA | |
| MW, pI | 40 kDa, 5.569 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1080 bp, 360 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | radA, yacL |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 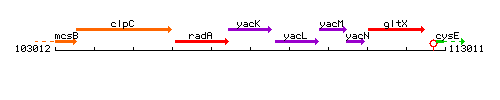
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, metabolism of signalling nucleotides, sporulation/ other, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB), cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), heat shock proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CtsR regulon, SigB regulon, SigM regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00880
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00880
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- synthesis of c-di-AMP from two molecules of ATP PubMed
- Protein family: disA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- contains a DAC domain for the synthesis of c-di-AMP PubMed
- Modification:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00880
- UniProt: P37573
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 314 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 393 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 465 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 179 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 232 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP987 (disA::tet), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- BKG2 (radA-disA::spc), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- 1A939 ( disA::tet), PubMed, available at BGSC
- Expression vector:
- IPTG inducible expression of His-disA in E. coli: pGP2563 (in pET19b), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Fabian Commichau's lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications