Difference between revisions of "MleA"
(→Extended information on the protein) |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
* '''Locus tag:''' BSU23550 | * '''Locus tag:''' BSU23550 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=mleA_2451463_2452782_-1 Expression] | ||
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
Revision as of 13:02, 25 January 2012
- Description: malic enzyme
| Gene name | mleA |
| Synonyms | yqkJ |
| Essential | no |
| Product | NAD-dependent malate dehydrogenase |
| Function | malate utilization |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 45 kDa, 4.895 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1317 bp, 439 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yqkK, mleN |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 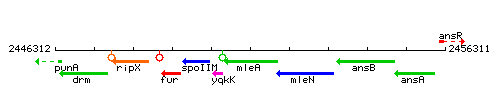
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of specific carbon sources
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU23550
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: (S)-malate + NAD+ = pyruvate + CO2 + NADH (according to Swiss-Prot) malate --> pyruvate
- Protein family: malic enzymes family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): YtsJ
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P54572
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 1.1.1.38
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP1136 (cat) available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References