Difference between revisions of "ClpC"
(→Extended information on the protein) |
|||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| + | * A mutation was found in this gene after evolution under relaxed selection for sporulation {{PubMed|21821766}} | ||
| Line 155: | Line 156: | ||
{{PubMed|19609260,19781636}} | {{PubMed|19609260,19781636}} | ||
==Original Publications== | ==Original Publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>9987115,8016067,9000055,12923101,10447896,9141693,2113920,16497325,19226326,8793870,10809708,14679237,17560370,11684022,8195092,11722737,11914365,12028382,18689476,19361434,9890793, 19767395 ,9987115, 11544224, 17981983, 14763982, 8016066 19361434 18689473 20070525 20923420 20852588 21622759 21368759</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>9987115,8016067,9000055,12923101,10447896,9141693,2113920,16497325,19226326,8793870,10809708,14679237,17560370,11684022,8195092,11722737,11914365,12028382,18689476,19361434,9890793, 19767395 ,9987115, 11544224, 17981983, 14763982, 8016066 19361434 18689473 20070525 20923420 20852588 21622759 21368759 21821766</pubmed> |
Additional publications: {{PubMed|18786145,16525504,17380125,16163393,12598648}} | Additional publications: {{PubMed|18786145,16525504,17380125,16163393,12598648}} | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 11:54, 15 August 2011
- Description: ATPase subunit of the ATP-dependent ClpC-ClpP protease, involved in competence development, heat shock regulation, motility, sporulation, protein quality control, biofilm formation
| Gene name | clpC |
| Synonyms | mecB |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ATPase subunit of the ClpC-ClpP protease |
| Function | protein degradation positive regulator of autolysin (LytC and LytD) synthesis |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: ClpC | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Stress | |
| MW, pI | 89 kDa, 5.746 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2430 bp, 810 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mcsB, radA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 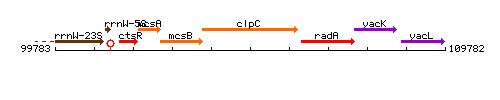
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
proteolysis, sporulation proteins, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB), heat shock proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CtsR regulon, SigB regulon, SigF regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00860
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
- A mutation was found in this gene after evolution under relaxed selection for sporulation PubMed
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATPase/chaperone
- Protein family: mecA family (according to Swiss-Prot) clpA/clpB family. ClpC subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot), AAA+ -type ATPase (IPR013093) InterPro (PF07724) PFAM
Targets of ClpC-ClpP-dependent protein degradation
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: AAA-ATPase PFAM
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: P37571
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion: C-terminal GFP fusions (single copy, also as CFP and YFP variants) available from the Hamoen Lab
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Leendert Hamoen, Newcastle University, UK homepage
Kürsad Turgay, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications
Christopher T Brown, Laura K Fishwick, Binna M Chokshi, Marissa A Cuff, Jay M Jackson, Travis Oglesby, Alison T Rioux, Enrique Rodriguez, Gregory S Stupp, Austin H Trupp, James S Woollcombe-Clarke, Tracy N Wright, William J Zaragoza, Jennifer C Drew, Eric W Triplett, Wayne L Nicholson
Whole-genome sequencing and phenotypic analysis of Bacillus subtilis mutants following evolution under conditions of relaxed selection for sporulation.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2011, 77(19);6867-77
[PubMed:21821766]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
A K W Elsholz, K Hempel, S Michalik, K Gronau, D Becher, M Hecker, U Gerth
Activity control of the ClpC adaptor McsB in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(15);3887-93
[PubMed:21622759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Feng Wang, Ziqing Mei, Yutao Qi, Chuangye Yan, Qi Hu, Jiawei Wang, Yigong Shi
Structure and mechanism of the hexameric MecA-ClpC molecular machine.
Nature: 2011, 471(7338);331-5
[PubMed:21368759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yunrong Chai, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
Reversal of an epigenetic switch governing cell chaining in Bacillus subtilis by protein instability.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 78(1);218-29
[PubMed:20923420]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alexander K W Elsholz, Stephan Michalik, Daniela Zühlke, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
CtsR, the Gram-positive master regulator of protein quality control, feels the heat.
EMBO J: 2010, 29(21);3621-9
[PubMed:20852588]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Mitsuo Ogura, Kensuke Tsukahara
Autoregulation of the Bacillus subtilis response regulator gene degU is coupled with the proteolysis of DegU-P by ClpCP.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 75(5);1244-59
[PubMed:20070525]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ziqing Mei, Feng Wang, Yutao Qi, Zhiyuan Zhou, Qi Hu, Han Li, Jiawei Wu, Yigong Shi
Molecular determinants of MecA as a degradation tag for the ClpCP protease.
J Biol Chem: 2009, 284(49);34366-75
[PubMed:19767395]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Douglas J Kojetin, Patrick D McLaughlin, Richele J Thompson, David Dubnau, Peter Prepiak, Mark Rance, John Cavanagh
Structural and motional contributions of the Bacillus subtilis ClpC N-domain to adaptor protein interactions.
J Mol Biol: 2009, 387(3);639-52
[PubMed:19361434]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jeanette Hahn, Naomi Kramer, Kenneth Briley, David Dubnau
McsA and B mediate the delocalization of competence proteins from the cell poles of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 72(1);202-15
[PubMed:19226326]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
James Kain, Gina G He, Richard Losick
Polar localization and compartmentalization of ClpP proteases during growth and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(20);6749-57
[PubMed:18689476]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lyle A Simmons, Alan D Grossman, Graham C Walker
Clp and Lon proteases occupy distinct subcellular positions in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(20);6758-68
[PubMed:18689473]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ulf Gerth, Holger Kock, Ilja Kusters, Stephan Michalik, Robert L Switzer, Michael Hecker
Clp-dependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(1);321-31
[PubMed:17981983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Peter Prepiak, David Dubnau
A peptide signal for adapter protein-mediated degradation by the AAA+ protease ClpCP.
Mol Cell: 2007, 26(5);639-47
[PubMed:17560370]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Stephanie T Wang, Barbara Setlow, Erin M Conlon, Jessica L Lyon, Daisuke Imamura, Tsutomu Sato, Peter Setlow, Richard Losick, Patrick Eichenberger
The forespore line of gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Biol: 2006, 358(1);16-37
[PubMed:16497325]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Holger Kock, Ulf Gerth, Michael Hecker
MurAA, catalysing the first committed step in peptidoglycan biosynthesis, is a target of Clp-dependent proteolysis in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 51(4);1087-102
[PubMed:14763982]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulf Gerth, Janine Kirstein, Jörg Mostertz, Torsten Waldminghaus, Marcus Miethke, Holger Kock, Michael Hecker
Fine-tuning in regulation of Clp protein content in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(1);179-91
[PubMed:14679237]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Qi Pan, Richard Losick
Unique degradation signal for ClpCP in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(17);5275-8
[PubMed:12923101]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Michiko M Nakano, Shunji Nakano, Peter Zuber
Spx (YjbD), a negative effector of competence in Bacillus subtilis, enhances ClpC-MecA-ComK interaction.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 44(5);1341-9
[PubMed:12028382]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Marjan Persuh, Ines Mandic-Mulec, David Dubnau
A MecA paralog, YpbH, binds ClpC, affecting both competence and sporulation.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(8);2310-3
[PubMed:11914365]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Turgay, M Persuh, J Hahn, D Dubnau
Roles of the two ClpC ATP binding sites in the regulation of competence and the stress response.
Mol Microbiol: 2001, 42(3);717-27
[PubMed:11722737]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Q Pan, D A Garsin, R Losick
Self-reinforcing activation of a cell-specific transcription factor by proteolysis of an anti-sigma factor in B. subtilis.
Mol Cell: 2001, 8(4);873-83
[PubMed:11684022]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Petersohn, M Brigulla, S Haas, J D Hoheisel, U Völker, M Hecker
Global analysis of the general stress response of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(19);5617-31
[PubMed:11544224]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Krüger, E Witt, S Ohlmeier, R Hanschke, M Hecker
The clp proteases of Bacillus subtilis are directly involved in degradation of misfolded proteins.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(11);3259-65
[PubMed:10809708]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Persuh, K Turgay, I Mandic-Mulec, D Dubnau
The N- and C-terminal domains of MecA recognize different partners in the competence molecular switch.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 33(4);886-94
[PubMed:10447896]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
I Derré, G Rapoport, T Msadek
CtsR, a novel regulator of stress and heat shock response, controls clp and molecular chaperone gene expression in gram-positive bacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 31(1);117-31
[PubMed:9987115]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Turgay, J Hahn, J Burghoorn, D Dubnau
Competence in Bacillus subtilis is controlled by regulated proteolysis of a transcription factor.
EMBO J: 1998, 17(22);6730-8
[PubMed:9890793]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
EIke Krüger, Tarek Msadek, Steffen Ohlmeier, Michael Hecker
The Bacillus subtilis clpC operon encodes DNA repair and competence proteins.
Microbiology (Reading): 1997, 143 ( Pt 4);1309-1316
[PubMed:9141693]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Turgay, L W Hamoen, G Venema, D Dubnau
Biochemical characterization of a molecular switch involving the heat shock protein ClpC, which controls the activity of ComK, the competence transcription factor of Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1997, 11(1);119-28
[PubMed:9000055]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Krüger, T Msadek, M Hecker
Alternate promoters direct stress-induced transcription of the Bacillus subtilis clpC operon.
Mol Microbiol: 1996, 20(4);713-23
[PubMed:8793870]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Kong, D Dubnau
Regulation of competence-specific gene expression by Mec-mediated protein-protein interaction in Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1994, 91(13);5793-7
[PubMed:8016067]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Msadek, F Kunst, G Rapoport
MecB of Bacillus subtilis, a member of the ClpC ATPase family, is a pleiotropic regulator controlling competence gene expression and growth at high temperature.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1994, 91(13);5788-92
[PubMed:8016066]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Krüger, U Völker, M Hecker
Stress induction of clpC in Bacillus subtilis and its involvement in stress tolerance.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(11);3360-7
[PubMed:8195092]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Roggiani, J Hahn, D Dubnau
Suppression of early competence mutations in Bacillus subtilis by mec mutations.
J Bacteriol: 1990, 172(7);4056-63
[PubMed:2113920]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Additional publications: PubMed