Difference between revisions of "SigW"
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Categories containing this gene/protein = | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[transcription]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[sigma factors and their control]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, W, X, Y)]]}} | ||
=The protein= | =The protein= | ||
Revision as of 19:55, 30 November 2010
- Description: RNA polymerase ECF-type sigma factor SigW
| Gene name | sigW |
| Synonyms | ybbL |
| Essential | no |
| Product | RNA polymerase ECF-type sigma factor SigW |
| Function | resistance against SdpC that functions in detoxification and/or production of antimicrobial compounds |
| MW, pI | 21 kDa, 8.614 |
| Gene length, protein length | 561 bp, 187 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | trnSL-Gln2, ybbM |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 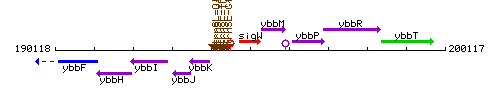
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU01730
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription, sigma factors and their control, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, W, X, Y)
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ECF subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Genes controlled by SigW
abh, pbpE-racX,xpaC-yaaN, yteI, yuaG, yknXYZ, ydjP, yfhM
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: RsiW acts as antagonist of SigW (anti-SigW)
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: Q45585
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
John Helmann, Cornell University, USA Homepage
Thomas Wiegert, University of Bayreuth, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References