Difference between revisions of "Eno"
(→Other original publications) |
(→Other original publications) |
||
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
==Other original publications== | ==Other original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed> 17726680, 17218307, 12850135, 19193632, 11489127, 8021172, 17505547, 25885, 20572937 | + | <pubmed> 17726680, 17218307, 12850135, 19193632, 11489127, 8021172, 17505547, 25885, 20572937 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 12:01, 5 July 2010
- Description: enolase, glycolytic/ gluconeogenic enzyme, universally conserved protein
| Gene name | eno |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | enolase |
| Function | enzyme in glycolysis/ gluconeogenesis |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 46,4 kDa, 4.49 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1290 bp, 430 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | yvbK, pgm |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 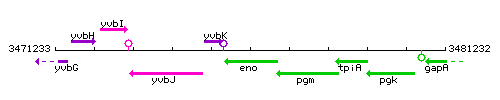
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU33900
Phenotypes of a mutant
- no growth on LB, requires glucose and malate
- essential according to Kobayashi et al. on LB PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 2-phospho-D-glycerate = phosphoenolpyruvate + H2O (according to Swiss-Prot) 2-phospho-D-glycerate = phosphoenolpyruvate + H(2)O
- Protein family: enolase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: reversible Michaelis-Menten PubMed
- Domains:
- substrate binding domain (366–369)
- Cofactor(s): Mg2+
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Inhibited by EDTA PubMed
Database entries
- Structure: 3ES8 (from Oceanobacillus iheyensis, complex with Mg(2+) and malate)
- UniProt: P37869
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 4.2.1.11
Additional information
- Enolase is a moonlighting protein. PubMed
- There are indications that this enzyme is an octamer PubMed
- universally conserved protein
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- pGP1426 (expression of eno in B. subtilis, in pBQ200), available in Stülke lab
- pGP399 (expression of eno from E. coli in B. subtilis, in pBQ200), available in Stülke lab
- pGP563 (N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844), available in Stülke lab
- pGP93 (N-terminal Strep-tag, purification from B. subtilis, for SPINE, in pGP380), available in Stülke lab
- pGP1500 (expression of pgm and eno in B. subtilis, in pBQ200), available in Stülke lab
- lacZ fusion:
- see pgk
- GFP fusion: pHT315-yfp-eno, available in Mijakovic lab
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody: available in Stülke lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Subcellular localization of enolase
Other original publications
Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Henrike Pförtner, Leonie Rempeters, Nico Pietack, Christina Herzberg, Jörg Stülke
The RNA degradosome in Bacillus subtilis: identification of CshA as the major RNA helicase in the multiprotein complex.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 77(4);958-71
[PubMed:20572937]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Fabian M Rothe, Christina Herzberg, Eva Wagner, Daniel Hellwig, Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Elke Hammer, Uwe Völker, Jörg Stülke
Novel activities of glycolytic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: interactions with essential proteins involved in mRNA processing.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2009, 8(6);1350-60
[PubMed:19193632]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Eymann, Dörte Becher, Jörg Bernhardt, Katrin Gronau, Anja Klutzny, Michael Hecker
Dynamics of protein phosphorylation on Ser/Thr/Tyr in Bacillus subtilis.
Proteomics: 2007, 7(19);3509-26
[PubMed:17726680]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Laurent Jannière, Danielle Canceill, Catherine Suski, Sophie Kanga, Bérengère Dalmais, Roxane Lestini, Anne-Françoise Monnier, Jérôme Chapuis, Alexander Bolotin, Marina Titok, Emmanuelle Le Chatelier, S Dusko Ehrlich
Genetic evidence for a link between glycolysis and DNA replication.
PLoS One: 2007, 2(5);e447
[PubMed:17505547]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Boris Macek, Ivan Mijakovic, Jesper V Olsen, Florian Gnad, Chanchal Kumar, Peter R Jensen, Matthias Mann
The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2007, 6(4);697-707
[PubMed:17218307]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Ludwig, G Homuth, M Schmalisch, F M Dyka, M Hecker, J Stülke
Transcription of glycolytic genes and operons in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for the presence of multiple levels of control of the gapA operon.
Mol Microbiol: 2001, 41(2);409-22
[PubMed:11489127]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M A Leyva-Vazquez, P Setlow
Cloning and nucleotide sequences of the genes encoding triose phosphate isomerase, phosphoglycerate mutase, and enolase from Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(13);3903-10
[PubMed:8021172]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R P Singh, P Setlow
Enolase from spores and cells of Bacillus megaterium: two-step purification of the enzyme and some of its properties.
J Bacteriol: 1978, 134(1);353-5
[PubMed:25885]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)