Difference between revisions of "PfkA"
(→Additional information) |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || 957 bp, 319 amino acids | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || 957 bp, 319 amino acids | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[ | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[pyk]]'', ''[[accA]]'' |
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Get the DNA and protein [http://srs.ebi.ac.uk/srsbin/cgi-bin/wgetz?-e+[EMBLCDS:CAB14879]+-newId sequences] <br/> (Barbe ''et al.'', 2009)''' | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Get the DNA and protein [http://srs.ebi.ac.uk/srsbin/cgi-bin/wgetz?-e+[EMBLCDS:CAB14879]+-newId sequences] <br/> (Barbe ''et al.'', 2009)''' | ||
Revision as of 09:19, 7 December 2009
- Description: phosphofructokinase, glycolytic enzyme
| Gene name | pfkA |
| Synonyms | pfk |
| Essential | yes |
| Product | 6-phosphofructokinase |
| Function | catabolic enzyme in glycolysis |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism, Sugar catabolism | |
| MW, pI | 34,1 kDa, 6.14 |
| Gene length, protein length | 957 bp, 319 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | pyk, accA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 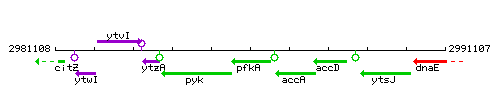
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29190
Phenotypes of a mutant
- Essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + D-fructose 6-phosphate = ADP + D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: phosphofructokinase family (according to Swiss-Prot) phosphofructokinase family
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: Allosteric Regulation (Reversible) PubMed
- Domains:
- 3 x nucleotide binding domain (ATP) (21–25), (154–158), (171–187)
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): Mg2+
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Inhibited by citrate, PEP (Hill Coefficient 3) and Ca2+ (competes with Mg2+) in B. licheniformes PubMed.
- Inhibited by ATP (competitively) and f6p (non-competitively) in G. stearothermophillus PubMed
- Activated by GDP and ADP in lower concentrations (1mM); above that inhibition, competing with the ATP for the binding site (in G. stearothermophillus) PubMed
- Activated by NH4+ PubMed
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot), Cytoplasm (Homogeneous) PubMed
Database entries
- Structure: 1MTO (mutant, complex with fructose-6-phosphate, Geobacillus stearothermophilus), 4PFK (Geobacillus stearothermophilus), Geobacillus stearothermophilus NCBI, Mutant form, complex with fructose-6-phosphate Geobacillus stearothermophilus NCBI
- UniProt: O34529
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.1.11
Additional information
PfkA is a moonlighting protein. PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation: twofold induced by glucose PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References