Difference between revisions of "FtsZ"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>15288790,15317782,12180929,9364910,10323866,19212404,15942012,12007411,16420366,16159787,10747015,16174771,16796675,10322023,9495766,9287012,1569582,10878122,11395470,10449747,17662947,12368265,18284588,8600030,18588879,7592498, 19136590 , 19429628, 19141479 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 19583568 15288790,15317782,12180929,9364910,10323866,19212404,15942012,12007411,16420366,16159787,10747015,16174771,16796675,10322023,9495766,9287012,1569582,10878122,11395470,10449747,17662947,12368265,18284588,8600030,18588879,7592498, 19136590 , 19429628, 19141479 </pubmed> |
Revision as of 07:44, 9 July 2009
- Description: cell-division initiation protein (septum formation)
| Gene name | ftsZ |
| Synonyms | ts-1 |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | cell-division initiation protein (septum formation) |
| Function | formation of Z-ring |
| MW, pI | 40 kDa, 4.814 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1146 bp, 382 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ftsA, bpr |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 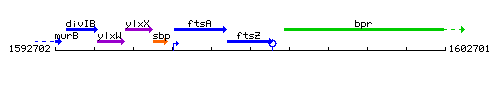
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15290
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ftsZ family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Swiss prot entry: P17865
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody: available in the Jeff Errington lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Imrich Barak, Slovak Academy of Science, Bratislava, Slovakia homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Tushar K Beuria, Parminder Singh, Avadhesha Surolia, Dulal Panda
Promoting assembly and bundling of FtsZ as a strategy to inhibit bacterial cell division: a new approach for developing novel antibacterial drugs.
Biochem J: 2009, 423(1);61-9
[PubMed:19583568]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Pamela Gamba, Jan-Willem Veening, Nigel J Saunders, Leendert W Hamoen, Richard A Daniel
Two-step assembly dynamics of the Bacillus subtilis divisome.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(13);4186-94
[PubMed:19429628]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
M Leaver, P Domínguez-Cuevas, J M Coxhead, R A Daniel, J Errington
Life without a wall or division machine in Bacillus subtilis.
Nature: 2009, 457(7231);849-53
[PubMed:19212404]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
James A Gregory, Eric C Becker, Kit Pogliano
Bacillus subtilis MinC destabilizes FtsZ-rings at new cell poles and contributes to the timing of cell division.
Genes Dev: 2008, 22(24);3475-88
[PubMed:19141479]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Daniel P Haeusser, Amy H Lee, Richard B Weart, Petra Anne Levin
ClpX inhibits FtsZ assembly in a manner that does not require its ATP hydrolysis-dependent chaperone activity.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(6);1986-91
[PubMed:19136590]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Dirk-Jan Scheffers
The effect of MinC on FtsZ polymerization is pH dependent and can be counteracted by ZapA.
FEBS Lett: 2008, 582(17);2601-8
[PubMed:18588879]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Aaron A Handler, Joo Eun Lim, Richard Losick
Peptide inhibitor of cytokinesis during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 68(3);588-99
[PubMed:18284588]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Richard B Weart, Amy H Lee, An-Chun Chien, Daniel P Haeusser, Norbert S Hill, Petra Anne Levin
A metabolic sensor governing cell size in bacteria.
Cell: 2007, 130(2);335-47
[PubMed:17662947]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Shu Ishikawa, Yoshikazu Kawai, Konosuke Hiramatsu, Masayoshi Kuwano, Naotake Ogasawara
A new FtsZ-interacting protein, YlmF, complements the activity of FtsA during progression of cell division in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 60(6);1364-80
[PubMed:16796675]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Leendert W Hamoen, Jean-Christophe Meile, Wouter de Jong, Philippe Noirot, Jeff Errington
SepF, a novel FtsZ-interacting protein required for a late step in cell division.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 59(3);989-99
[PubMed:16420366]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Neil R Stokes, Jörg Sievers, Stephanie Barker, James M Bennett, David R Brown, Ian Collins, Veronica M Errington, David Foulger, Michelle Hall, Rowena Halsey, Hazel Johnson, Valerie Rose, Helena B Thomaides, David J Haydon, Lloyd G Czaplewski, Jeff Errington
Novel inhibitors of bacterial cytokinesis identified by a cell-based antibiotic screening assay.
J Biol Chem: 2005, 280(48);39709-15
[PubMed:16174771]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S O Jensen, L S Thompson, E J Harry
Cell division in Bacillus subtilis: FtsZ and FtsA association is Z-ring independent, and FtsA is required for efficient midcell Z-Ring assembly.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(18);6536-44
[PubMed:16159787]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Andrea Feucht, Jeffery Errington
ftsZ mutations affecting cell division frequency, placement and morphology in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2005, 151(Pt 6);2053-2064
[PubMed:15942012]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
David E Anderson, Frederico J Gueiros-Filho, Harold P Erickson
Assembly dynamics of FtsZ rings in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli and effects of FtsZ-regulating proteins.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(17);5775-81
[PubMed:15317782]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Harry H Low, Martin C Moncrieffe, Jan Löwe
The crystal structure of ZapA and its modulation of FtsZ polymerisation.
J Mol Biol: 2004, 341(3);839-52
[PubMed:15288790]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Frederico J Gueiros-Filho, Richard Losick
A widely conserved bacterial cell division protein that promotes assembly of the tubulin-like protein FtsZ.
Genes Dev: 2002, 16(19);2544-56
[PubMed:12368265]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Andrea Feucht, Laura Abbotts, Jeffery Errington
The cell differentiation protein SpoIIE contains a regulatory site that controls its phosphatase activity in response to asymmetric septation.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 45(4);1119-30
[PubMed:12180929]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Sigal Ben-Yehuda, Richard Losick
Asymmetric cell division in B. subtilis involves a spiral-like intermediate of the cytokinetic protein FtsZ.
Cell: 2002, 109(2);257-66
[PubMed:12007411]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P L Graumann, R Losick
Coupling of asymmetric division to polar placement of replication origin regions in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(13);4052-60
[PubMed:11395470]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Keisuke Fukuchi, Yasuhiro Kasahara, Kei Asai, Kazuo Kobayashi, Shigeki Moriya, Naotake Ogasawara
The essential two-component regulatory system encoded by yycF and yycG modulates expression of the ftsAZ operon in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2000, 146 ( Pt 7);1573-1583
[PubMed:10878122]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
I Lucet, A Feucht, M D Yudkin, J Errington
Direct interaction between the cell division protein FtsZ and the cell differentiation protein SpoIIE.
EMBO J: 2000, 19(7);1467-75
[PubMed:10747015]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P A Levin, I G Kurtser, A D Grossman
Identification and characterization of a negative regulator of FtsZ ring formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1999, 96(17);9642-7
[PubMed:10449747]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N King, O Dreesen, P Stragier, K Pogliano, R Losick
Septation, dephosphorylation, and the activation of sigmaF during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1999, 13(9);1156-67
[PubMed:10323866]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L B Pedersen, E R Angert, P Setlow
Septal localization of penicillin-binding protein 1 in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(10);3201-11
[PubMed:10322023]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Khvorova, L Zhang, M L Higgins, P J Piggot
The spoIIE locus is involved in the Spo0A-dependent switch in the location of FtsZ rings in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(5);1256-60
[PubMed:9495766]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P A Levin, R Losick, P Stragier, F Arigoni
Localization of the sporulation protein SpoIIE in Bacillus subtilis is dependent upon the cell division protein FtsZ.
Mol Microbiol: 1997, 25(5);839-46
[PubMed:9364910]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
X Wang, J Huang, A Mukherjee, C Cao, J Lutkenhaus
Analysis of the interaction of FtsZ with itself, GTP, and FtsA.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(17);5551-9
[PubMed:9287012]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P A Levin, R Losick
Transcription factor Spo0A switches the localization of the cell division protein FtsZ from a medial to a bipolar pattern in Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1996, 10(4);478-88
[PubMed:8600030]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M A Strauch
Delineation of AbrB-binding sites on the Bacillus subtilis spo0H, kinB, ftsAZ, and pbpE promoters and use of a derived homology to identify a previously unsuspected binding site in the bsuB1 methylase promote.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(23);6999-7002
[PubMed:7592498]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Gonzy-Tréboul, C Karmazyn-Campelli, P Stragier
Developmental regulation of transcription of the Bacillus subtilis ftsAZ operon.
J Mol Biol: 1992, 224(4);967-79
[PubMed:1569582]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)