Difference between revisions of "CdaA"
(→Reviews) |
(→Original publications) |
||
| Line 160: | Line 160: | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>12884008,21566650, 23192352 22211522 25605729 25616256</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>12884008,21566650, 23192352 22211522 25605729 25616256 26240071 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 12:59, 5 August 2015
- Description: diadenylate cyclase, synthesis of c-di-AMP in vegetative cells
| Gene name | cdaA |
| Synonyms | ybbP, ybbQ |
| Essential | no |
| Product | diadenylate cyclase |
| Function | synthesis of c-di-AMP |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: cdaA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: CdaA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: cdaA | |
| MW, pI | 30 kDa, 8.074 |
| Gene length, protein length | 819 bp, 273 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | rsiW, cdaR |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 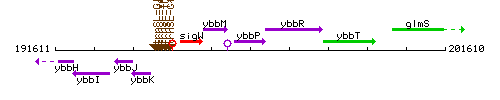
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
membrane proteins, metabolism of signalling nucleotides
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU01750
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU01750
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- synthesis of c-di-AMP from two molecules of ATP PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s): CdaS
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- contains a DAC domain involved in the synthesis of c-di-AMP PubMed
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU01750
- Structure: 4RV7 (the DAC domain and C-terminal domain of CdaA from Listeria monocytogenes (aa 101 - 273), 65% identity) PubMed
- UniProt: Q45589
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP94 (DcdaA::spc), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP997 (cdaA::cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP985 (cdaA-cdaR::cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- expression of native cdaA in B. subtilis: pGP1960 (in pBQ200), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- expression of cdaA-Strep in B. subtilis suitable for SPINE: pGP1986 (in pGP382), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- IPTG inducible expression of cdaA-Strep in E. coli: pGP2564 (in pGP574), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion: GP1339 (cat) based on pAC6, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab. Respective plasmid: pGP1990.
- FLAG-tag construct:
- GP1381 cdaA-3xFLAG ermC (based on pGP1087), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Jan Gundlach, Felix M P Mehne, Christina Herzberg, Jan Kampf, Oliver Valerius, Volkhard Kaever, Jörg Stülke
An Essential Poison: Synthesis and Degradation of Cyclic Di-AMP in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2015, 197(20);3265-74
[PubMed:26240071]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Carolina Gándara, Juan C Alonso
DisA and c-di-AMP act at the intersection between DNA-damage response and stress homeostasis in exponentially growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
DNA Repair (Amst): 2015, 27;1-8
[PubMed:25616256]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jonathan Rosenberg, Achim Dickmanns, Piotr Neumann, Katrin Gunka, Johannes Arens, Volkhard Kaever, Jörg Stülke, Ralf Ficner, Fabian M Commichau
Structural and biochemical analysis of the essential diadenylate cyclase CdaA from Listeria monocytogenes.
J Biol Chem: 2015, 290(10);6596-606
[PubMed:25605729]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Felix M P Mehne, Katrin Gunka, Hinnerk Eilers, Christina Herzberg, Volkhard Kaever, Jörg Stülke
Cyclic di-AMP homeostasis in bacillus subtilis: both lack and high level accumulation of the nucleotide are detrimental for cell growth.
J Biol Chem: 2013, 288(3);2004-17
[PubMed:23192352]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yun Luo, John D Helmann
Analysis of the role of Bacillus subtilis σ(M) in β-lactam resistance reveals an essential role for c-di-AMP in peptidoglycan homeostasis.
Mol Microbiol: 2012, 83(3);623-39
[PubMed:22211522]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yaara Oppenheimer-Shaanan, Ezequiel Wexselblatt, Jehoshua Katzhendler, Eylon Yavin, Sigal Ben-Yehuda
c-di-AMP reports DNA integrity during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
EMBO Rep: 2011, 12(6);594-601
[PubMed:21566650]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
G Hambraeus, C von Wachenfeldt, L Hederstedt
Genome-wide survey of mRNA half-lives in Bacillus subtilis identifies extremely stable mRNAs.
Mol Genet Genomics: 2003, 269(5);706-14
[PubMed:12884008]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)