Difference between revisions of "SinR"
(→Original publications) |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || transcriptional regulator ([[transcription factors of the Xre family|Xre family]]) of post-exponential-phase responses genes | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || transcriptional regulator ([[transcription factors of the Xre family|Xre family]]) |
| + | of post-exponential-phase responses genes | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || control of [[biofilm formation]] | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || control of [[biofilm formation]] | ||
Revision as of 14:30, 30 November 2014
- Description: transcriptional regulator (Xre family) of post-exponential-phase responses genes
| Gene name | sinR |
| Synonyms | sin, flaD |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional regulator (Xre family)
of post-exponential-phase responses genes |
| Function | control of biofilm formation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: sinR | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SinR | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: sinR | |
| MW, pI | 12 kDa, 7.177 |
| Gene length, protein length | 333 bp, 111 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | sinI, tasA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 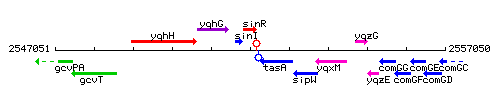
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, transition state regulators, biofilm formation
This gene is a member of the following regulons
AbrB regulon, ScoC regulon, Spo0A regulon
The SinR regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU24610
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU24610
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- transcription regulator of biofilm genes, acts as a true repressor of the tapA-sipW-tasA operon and as an anti-activator (prevents binding of the activator protein RemA) of the epsA-epsB-epsC-epsD-epsE-epsF-epsG-epsH-epsI-epsJ-epsK-epsL-epsM-epsN-epsO operon PubMed
- acts as co-repressor for SlrR PubMed
- Protein family:Xre family
- Paralogous protein(s): SlrR
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU24610
- Structure:
- UniProt: P06533
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- the mRNA is substantially stabilized upon depletion of RNase Y (the half-life of the mRNA increases from 3.5 to 13 min) PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 699 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 425 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP923 (sinR::spec) PubMed, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP736 (sinR::tetR) PubMed, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- 1S97 (sinR::phleo), PubMed, available at BGSC
- GP1672 (sinR-tasA::cat) PubMed, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP1663 (yghG-sinI-sinR-tasA), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, expression in B. subtilis, in pGP380: pGP1083 , available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- FLAG-tag construct: GP960 (spc, based on pGP1331), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Modelling of the SinI/SinR switch
Jennifer S Hallinan, Goksel Misirli, Anil Wipat
Evolutionary computation for the design of a stochastic switch for synthetic genetic circuits.
Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc: 2010, 2010;768-74
[PubMed:21095906]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications