Difference between revisions of "RecA"
(→Original publications) |
(→Biological materials) |
||
| Line 159: | Line 159: | ||
* '''GFP fusion:''' | * '''GFP fusion:''' | ||
| − | * '''two-hybrid system:''' | + | * '''two-hybrid system:''' B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system ([[BACTH]]), available in [[Fabian Commichau]]'s lab |
* '''Antibody:''' | * '''Antibody:''' | ||
Revision as of 13:33, 7 October 2014
- Description: multifunctional protein involved in homologous recombination and DNA repair (LexA-autocleavage), required to internalize and to recombine ssDNA with homologous resident duplex
| Gene name | recA |
| Synonyms | recE |
| Essential | no |
| Product | multifunctional protein involved in homologous recombination and DNA repair (LexA-autocleavage) |
| Function | DNA repair/ recombination |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: recA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: RecA | |
| MW, pI | 37 kDa, 4.883 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1041 bp, 347 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | cinA, pbpX |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 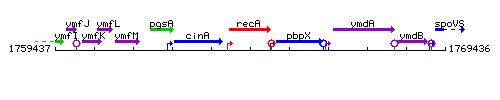
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
DNA repair/ recombination, genetic competence, phosphoproteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16940
Phenotypes of a mutant
- drastically reduced survival of mature dormant spores after exposure to ultrahigh vacuum desiccation and ionizing radiation that induce single strand (ss) DNA nicks and double-strand breaks (DSBs) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16940
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
RecA filaments are dismantled from DNA by PcrA PubMed
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: recA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- colocalizes to the replisome in response to endogenous and exogenous DNA damage and in response to damage-independent fork arrest (formation of DNA repair centers), repair center formation depends on RecO and RecR, and is facilitated by RecF and SsbA PubMed
- Nucleoid (Mid-cell) PubMed
- localizes to one cell pole PubMed
- forms a transient, mobile focus associated with the chromosome during spore development PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16940
- Structure: 1U94 (RecA from E. coli, 62% identity, 86% similarity)
- UniProt: P16971
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: recA PubMed
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 417 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1257 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 5143 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 3169 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 4953 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- IRN444 (cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- 1A746 (recA::erm), PubMed, available at BGSC
- 1A786 (recA::kan), PubMed, available at BGSC
- BP469 (recA::erm), available in Fabian Commichau's lab
- Expression vector: for expression, purification in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, pRSETA available in Ulf Gerth's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Fabian Commichau's lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Peter Graumann, Freiburg University, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications