Difference between revisions of "PnpA"
(→Biological materials) |
|||
| Line 141: | Line 141: | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | * '''Mutant:''' GP584 (aphA3), available in [[Stülke]] lab | + | * '''Mutant:''' GP584 (aphA3), available in [[Jörg Stülke]]'s lab |
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
Revision as of 15:56, 17 August 2014
- Description: polynucleotide phosphorylase, RNase, involved in double-strand break repair
| Gene name | pnpA |
| Synonyms | comR |
| Essential | no |
| Product | polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase) (EC 2.7.7.8) |
| Function | DNA repair, competence development, RNA degradation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: pnpA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: PnpA | |
| MW, pI | 77 kDa, 4.89 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2115 bp, 705 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | rpsO, ylxY |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 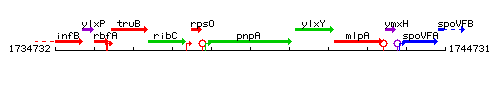
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
genetic competence, DNA repair/ recombination, Rnases, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16690
Phenotypes of a mutant
- The pnpA mutant is cold sensitive and sensitive to tetracyclin, it shows multiseptate filamentous growth. PubMed
- The mutant is deficient in genetic competence (no expression of the late competence genes) PubMed
- The mutant overexpresses the trp and putB-putC-putP operons.
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16690
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- 3'-5' exoribonuclease, RNase
- PNPase degrades the trp mRNA from the RNA-TRAP complex
- involved in double-strand break (DSB) repair via homologous recombination (HR) or non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) PubMed
- degrades ssDNA (3' --> 5') (stimulated by RecA, inhibited by SsbA) PubMed
- can polymerize ssDNA at a free 3' OH end, stimulated by RecN PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16690
- Structure: 3CDI (protein from E. coli), 3GCM (protein from E. coli, PNPase/RNase E micro-domain/RNA tetragonal crystal form )
- UniProt: P50849
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
required for the expression of late competence genes comGA and comK, requirement bypassed by a mecA disruption; may be necessary for modification of the srfAA transcript (stabilization or translation activation)
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 3793 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 8647 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 2302 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2327 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 2689 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP584 (aphA3), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- for expression, purification in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP838, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- for expression/ purification from B. subtilis with N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, in pGP380: pGP1342, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- for chromosomal expression of PnpA-Strep (cat): GP1002, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- for chromosomal expression of PnpA-Strep (spc): GP1038, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- FLAG-tag construct:
- GP1021 (spc, based on pGP1331), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP1076 (ermC), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
David Bechhofer, Mount Sinai School, New York, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
PNPase in E. coli