Difference between revisions of "AccA"
(→Reviews) |
|||
| Line 148: | Line 148: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
==Reviews== | ==Reviews== | ||
| − | <pubmed> 15952903, 17919287 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 15952903, 17919287 12121720 </pubmed> |
==Original Publications== | ==Original Publications== | ||
Revision as of 16:38, 5 June 2014
- Description: acetyl-CoA carboxylase (alpha subunit)
| Gene name | accA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | acetyl-CoA carboxylase (alpha subunit)) |
| Function | production of malonyl-CoA, the substrate for fatty acid biosynthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: accA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: AccA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: accA | |
| MW, pI | 36 kDa, 6.087 |
| Gene length, protein length | 975 bp, 325 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | pfkA, accD |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 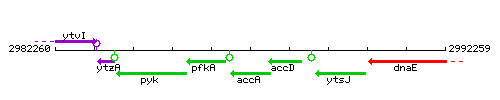
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed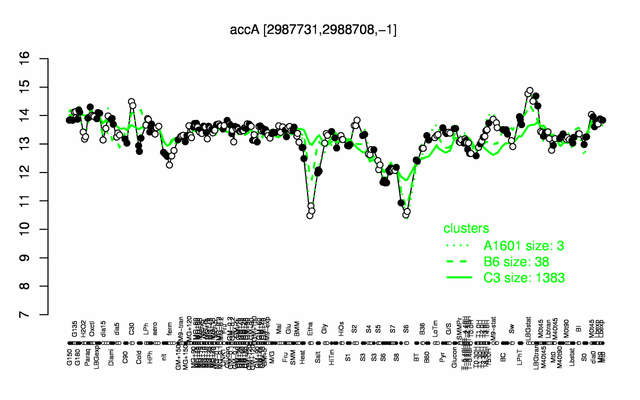
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis of lipids, essential genes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29200
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29200
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + acetyl-CoA + HCO3- = ADP + phosphate + malonyl-CoA (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: accA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot), Membrane-proximal (Spotty) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29200
- UniProt: O34847
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 6.4.1.2
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1047 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 795 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 910 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications