Difference between revisions of "FrlD"
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
** the ''[[frlB]]-[[frlO]]-[[frlN]]-[[frlM]]-[[frlD]]'' operon is not expressed in a ''[[cshA]]'' mutant {{PubMed|23175651}} | ** the ''[[frlB]]-[[frlO]]-[[frlN]]-[[frlM]]-[[frlD]]'' operon is not expressed in a ''[[cshA]]'' mutant {{PubMed|23175651}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 828 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 828 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 9042 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 3514 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 4350 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
Revision as of 14:21, 17 April 2014
- Description: fructosamine kinase
| Gene name | frlD |
| Synonyms | yurL |
| Essential | no |
| Product | fructosamine kinase |
| Function | metabolism of sugar amines |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: frlD | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: frlD | |
| MW, pI | 30 kDa, 4.909 |
| Gene length, protein length | 852 bp, 284 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | frlR, frlM |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 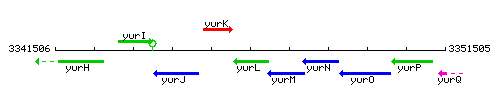
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed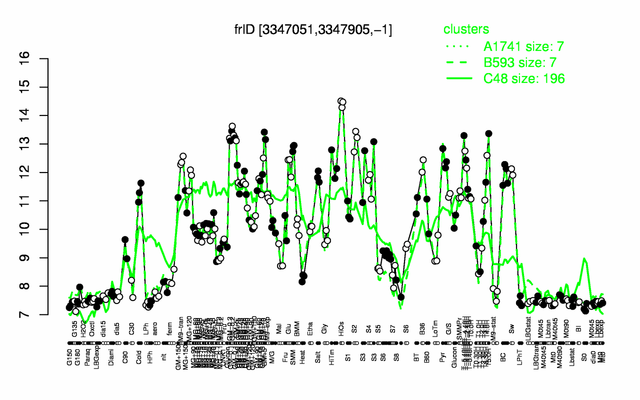
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of specific carbon sources, utilization of nitrogen sources other than amino acids
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU32570
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU32570
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: carbohydrate kinase pfkB family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU32570
- Structure:
- UniProt: O32153
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- the mRNA is substantially stabilized upon depletion of RNase Y PubMed
- the frlB-frlO-frlN-frlM-frlD operon is not expressed in a cshA mutant PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 828 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 9042 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 3514 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 4350 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Leonie Rempeters, Ákos T Kovács, Christoph Wrede, Claudia Baierlein, Heike Krebber, Oscar P Kuipers, Jörg Stülke
DEAD-Box RNA helicases in Bacillus subtilis have multiple functions and act independently from each other.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(3);534-44
[PubMed:23175651]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Marc Schaffer, Ulrike Mäder, Christine Diethmaier, Christina Herzberg, Jörg Stülke
RNA processing in Bacillus subtilis: identification of targets of the essential RNase Y.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 81(6);1459-73
[PubMed:21815947]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Veronika Maria Deppe, Stephanie Klatte, Johannes Bongaerts, Karl-Heinz Maurer, Timothy O'Connell, Friedhelm Meinhardt
Genetic control of amadori product degradation in Bacillus subtilis via regulation of frlBONMD expression by FrlR.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2011, 77(9);2839-46
[PubMed:21398478]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Veronika Maria Deppe, Johannes Bongaerts, Timothy O'Connell, Karl-Heinz Maurer, Friedhelm Meinhardt
Enzymatic deglycation of Amadori products in bacteria: mechanisms, occurrence and physiological functions.
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol: 2011, 90(2);399-406
[PubMed:21347729]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Elsa Wiame, Pedro Lamosa, Helena Santos, Emile Van Schaftingen
Identification of glucoselysine-6-phosphate deglycase, an enzyme involved in the metabolism of the fructation product glucoselysine.
Biochem J: 2005, 392(Pt 2);263-9
[PubMed:16153181]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Elsa Wiame, Armelle Duquenne, Ghislain Delpierre, Emile Van Schaftingen
Identification of enzymes acting on alpha-glycated amino acids in Bacillus subtilis.
FEBS Lett: 2004, 577(3);469-72
[PubMed:15556630]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Yoshiko Nakaura, Robert P Shivers, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Richard Losick, Yasutaro Fujita, Abraham L Sonenshein
Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(6);1911-22
[PubMed:12618455]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)