Difference between revisions of "ClpC"
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1157 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1157 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2624 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2624 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 711 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 495 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 617 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' ''[[clpC]]::tet'' available from the [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/wiki/index.php/Leendert_Hamoen Hamoen] Lab | * '''Mutant:''' ''[[clpC]]::tet'' available from the [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/wiki/index.php/Leendert_Hamoen Hamoen] Lab | ||
Revision as of 14:04, 17 April 2014
- Description: ATPase subunit of the ATP-dependent ClpC-ClpP protease, involved in competence development, heat shock regulation, motility, sporulation, protein quality control, biofilm formation
| Gene name | clpC |
| Synonyms | mecB |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ATPase subunit of the ClpC-ClpP protease |
| Function | protein degradation positive regulator of autolysin (LytC and LytD) synthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: clpC | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: ClpC | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: clpC | |
| MW, pI | 89 kDa, 5.746 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2430 bp, 810 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mcsB, radA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 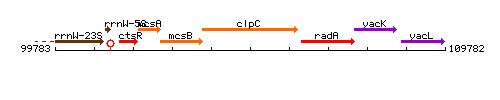
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
proteolysis, sporulation proteins, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB), heat shock proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CtsR regulon, SigB regulon, SigF regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00860
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00860
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
- A mutation was found in this gene after evolution under relaxed selection for sporulation PubMed
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATPase/chaperone
- Protein family: mecA family (according to Swiss-Prot) clpA/clpB family. ClpC subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot), AAA+ -type ATPase (IPR013093) InterPro (PF07724) PFAM
Targets of ClpC-ClpP-dependent protein degradation
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on Arg-5 and Arg-254 PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00860
- UniProt: P37571
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 1157 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2624 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 711 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 495 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 617 PubMed
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion: C-terminal GFP fusions (single copy, also as CFP and YFP variants) available from the Hamoen Lab
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Leendert Hamoen, Newcastle University, UK homepage
Kürsad Turgay, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Noël Molière, Kürşad Turgay
General and regulatory proteolysis in Bacillus subtilis.
Subcell Biochem: 2013, 66;73-103
[PubMed:23479438]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Aurelia Battesti, Susan Gottesman
Roles of adaptor proteins in regulation of bacterial proteolysis.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2013, 16(2);140-7
[PubMed:23375660]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Noël Molière, Kürşad Turgay
Chaperone-protease systems in regulation and protein quality control in Bacillus subtilis.
Res Microbiol: 2009, 160(9);637-44
[PubMed:19781636]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Janine Kirstein, Noël Molière, David A Dougan, Kürşad Turgay
Adapting the machine: adaptor proteins for Hsp100/Clp and AAA+ proteases.
Nat Rev Microbiol: 2009, 7(8);589-99
[PubMed:19609260]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Dorte Frees, Kirsi Savijoki, Pekka Varmanen, Hanne Ingmer
Clp ATPases and ClpP proteolytic complexes regulate vital biological processes in low GC, Gram-positive bacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 63(5);1285-95
[PubMed:17302811]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original Publications