Difference between revisions of "Abh"
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU14480&redirect=T BSU14480] | ||
* '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/abh.html] | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/abh.html] | ||
| Line 100: | Line 101: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU14480&redirect=T BSU14480] | ||
* '''Structure:''' [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2FY9 2FY9] (N-terminal DNA recognition domain) | * '''Structure:''' [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2FY9 2FY9] (N-terminal DNA recognition domain) | ||
Revision as of 13:36, 2 April 2014
- Description: transcriptional regulator of transition state genes
| Gene name | abh |
| Synonyms | ylxT, yzaA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional regulator |
| Function | regulation of gene expression during the transition from growth to stationary phase |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: abh | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: Abh | |
| MW, pI | 10 kDa, 5.753 |
| Gene length, protein length | 276 bp, 92 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mreBH, kinC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 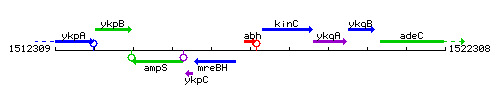
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed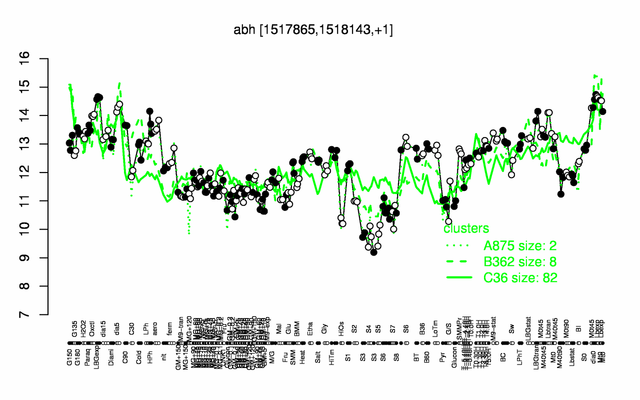
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transition state regulators, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y)
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The Abh regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU14480
Phenotypes of a mutant
- inactivation of abh results in sensitivity against beta-lactam antibiotics that can be restored by induction of slrR expression or by inactivation of the genes encoding major autolysins (lytC, lytF) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU14480
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
Genes controlled by Abh
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU14480
- Structure: 2FY9 (N-terminal DNA recognition domain)
- UniProt: P39758
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Mark Strauch, Baltimore, USA homepage
Your additional remarks
References
The Abh regulon: PubMed
Other original publications