Difference between revisions of "SinI"
(→Expression and regulation) |
(→Original publications) |
||
| Line 146: | Line 146: | ||
<pubmed> 21095906 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 21095906 </pubmed> | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>3125149 15661000,18047568,,11751836,1906467,11751836,7635837,11751836, 10547280, 15104138, 9799632 20923420 8422983 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>3125149 15661000,18047568,,11751836,1906467,11751836,7635837,11751836, 10547280, 15104138, 9799632 20923420 8422983 21326214</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 09:25, 18 February 2011
| Gene name | sinI |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | antagonist of SinR |
| Function | control of biofilm formation |
| Regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Biofilm | |
| MW, pI | 6 kDa, 6.333 |
| Gene length, protein length | 171 bp, 57 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yqhG, sinR |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 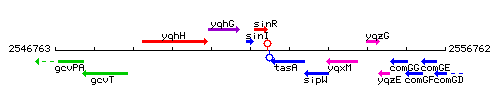
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, transition state regulators, biofilm formation
This gene is a member of the following regulons
AbrB regulon, ScoC regulon, Spo0A regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU24600
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s): SlrA
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- UniProt: P23308
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Modelling of the SinI/SinR switch
Original publications