Difference between revisions of "PhoP"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
* '''Activation by PhoP:''' ''[[phoP]]-[[phoR]]'' {{PubMed|14762014}}, ''[[pstS]]-[[pstC]]-[[pstA]]-[[pstBA]]-[[pstBB]]'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/9098050 PubMed] | * '''Activation by PhoP:''' ''[[phoP]]-[[phoR]]'' {{PubMed|14762014}}, ''[[pstS]]-[[pstC]]-[[pstA]]-[[pstBA]]-[[pstBB]]'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/9098050 PubMed] | ||
| − | |||
* '''Repression by PhoP:''' | * '''Repression by PhoP:''' | ||
| Line 105: | Line 104: | ||
** carbon catabolite repression ([[CcpA]]) {{PubMed|16452408,12850135}} | ** carbon catabolite repression ([[CcpA]]) {{PubMed|16452408,12850135}} | ||
** expressed under conditions of phosphate limitation ([[PhoP]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15205429,14762014 PubMed] | ** expressed under conditions of phosphate limitation ([[PhoP]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15205429,14762014 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** expressed in post-exponential phase ([[ScoC]]) {{PubMed|20382764}} | ||
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | ||
** [[CcpA]]: transcription repression {{PubMed|16452408,12850135}} | ** [[CcpA]]: transcription repression {{PubMed|16452408,12850135}} | ||
** [[PhoP]]: transcription activation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15205429,14762014 PubMed] | ** [[PhoP]]: transcription activation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/15205429,14762014 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** [[ScoC]]: transcription repression {{PubMed|20382764}} | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
| Line 133: | Line 134: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>15576792,10433720,9611818,15205429,16030210,17085571,16452408,9593301,9098050,14973033,10094672,12486062,10094677,10913081,9988472,12486063,9457886,9683503,9680208,9335276,15205429,14762014,12850135, 20059685 20167622 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>15576792,10433720,9611818,15205429,16030210,17085571,16452408,9593301,9098050,14973033,10094672,12486062,10094677,10913081,9988472,12486063,9457886,9683503,9680208,9335276,15205429,14762014,12850135, 20059685 20167622 20382764 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 11:33, 13 April 2010
- Description: two-component response regulator, regulation of phosphate metabolism
| Gene name | phoP |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component response regulator |
| Function | regulation of phosphate metabolism (phoA, phoB, phoD, resABCDE, tagA-tagB, tagDEF, tuaA-H) |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Folate | |
| MW, pI | 27 kDa, 5.068 |
| Gene length, protein length | 720 bp, 240 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | phoR, mdh |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 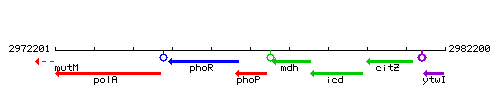
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29110
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Genes controlled by PhoP
- Repression by PhoP:
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation by PhoR under conditions of phosphate limitation (stimulates DNA-binding activity)
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: phosphorylation stimulates DNA-binding activity
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure: 1MVO (receiver domain)
- UniProt: P13792
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Marion Hulett, University of Illinois at Chicago, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References