Difference between revisions of "RocA"
(→Database entries) |
|||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''Structure:''' | + | * '''Structure:''' [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/cgi/explore.cgi?pdbId=2BJA2BJA] (with bound NADH from ''Thermus thermophilus'', 43% identity, 59% similarity) {{PubMed|16934832}} |
* '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P39634 P39634] | * '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P39634 P39634] | ||
Revision as of 17:59, 18 February 2010
- Description: 3-hydroxy-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase
| Gene name | rocA |
| Synonyms | ipa-76d |
| Essential | no |
| Product | 3-hydroxy-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase |
| Function | arginine, ornithine and citrulline utilization |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Ammonium/ glutamate | |
| MW, pI | 56 kDa, 5.58 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1545 bp, 515 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | rocB, rocG |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 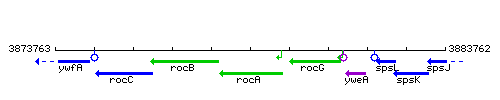
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU37780
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate + NAD(P)+ + 2 H2O = L-glutamate + NAD(P)H (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: RocA subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation on (Thr-2 OR Thr-4 OR Tyr-5) PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- UniProt: P39634
- KEGG entry: [4]
- E.C. number: 1.5.1.12
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Boris Macek, Ivan Mijakovic, Jesper V Olsen, Florian Gnad, Chanchal Kumar, Peter R Jensen, Matthias Mann
The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2007, 6(4);697-707
[PubMed:17218307]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Yoshiko Nakaura, Robert P Shivers, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Richard Losick, Yasutaro Fujita, Abraham L Sonenshein
Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(6);1911-22
[PubMed:12618455]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
U Klingel, C M Miller, A K North, P G Stockley, S Baumberg
A binding site for activation by the Bacillus subtilis AhrC protein, a repressor/activator of arginine metabolism.
Mol Gen Genet: 1995, 248(3);329-40
[PubMed:7565595]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Calogero, R Gardan, P Glaser, J Schweizer, G Rapoport, M Debarbouille
RocR, a novel regulatory protein controlling arginine utilization in Bacillus subtilis, belongs to the NtrC/NifA family of transcriptional activators.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(5);1234-41
[PubMed:8113162]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)