Difference between revisions of "PolY1"
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' translesion synthesis (TLS-) DNA polymerase Y1, important for stationary phase mutagenesis <br/><br/> | + | * '''Description:''' translesion synthesis (TLS-) DNA polymerase Y1, important for stationary phase mutagenesis, promotes efficient [[replisome]] progression through lagging-strand genes, thereby reducing potentially detrimental breaks and single-stranded DNA at these loci <br/><br/> |
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| − | + | <br/><br/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
| Line 62: | Line 58: | ||
reduced UV-induced mutagenesis {{PubMed|12644484}} | reduced UV-induced mutagenesis {{PubMed|12644484}} | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU23870&redirect=T BSU23870] | ||
* '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/yqjHI.html] | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/yqjHI.html] | ||
| Line 68: | Line 65: | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 101: | Line 96: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU23870&redirect=T BSU23870] | ||
* '''Structure:''' | * '''Structure:''' | ||
| Line 148: | Line 144: | ||
<pubmed> 22933559 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 22933559 </pubmed> | ||
== Original publications == | == Original publications == | ||
| − | <pubmed> 12644484 15469515 16045613 19924481 23686288 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 12644484 15469515 16045613 19924481 23686288 25713353</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:18, 3 March 2015
- Description: translesion synthesis (TLS-) DNA polymerase Y1, important for stationary phase mutagenesis, promotes efficient replisome progression through lagging-strand genes, thereby reducing potentially detrimental breaks and single-stranded DNA at these loci
| Gene name | polY1 |
| Synonyms | yqjH |
| Essential | no |
| Product | translesion synthesis (TLS-) DNA polymerase Y1 |
| Function | generation of mutations in stationary phase |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: polY1 | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: PolY1 | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: polY1 | |
| MW, pI | 46 kDa, 9.953 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1242 bp, 414 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | gndA, mifM |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 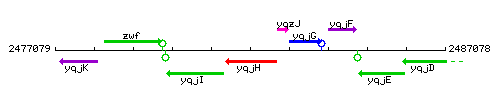
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU23870
Phenotypes of a mutant
reduced UV-induced mutagenesis PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU23870
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNA(n) = diphosphate + DNA(n+1) (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: DNA polymerase type-Y family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (homogeneous)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU23870
- Structure:
- UniProt: P54545
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.7.7
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation: constitutively expressed PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP1111 (spc), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications