Difference between revisions of "FlgM"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 150: | Line 150: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | <pubmed>8955328,19898538 8412657 8045879 , 20233303 10207036 8655488 23352839 21736639</pubmed> | |
| − | <pubmed>8955328,19898538 8412657 8045879 , 20233303 10207036 8655488 23352839 </pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 14:42, 8 April 2014
- Description: anti-SigD, regulation of flagellin, motility, and chemotaxis
| Gene name | flgM |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | anti-SigD |
| Function | control of SigD activity |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: flgM | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: FlgM | |
| MW, pI | 9 kDa, 9.918 |
| Gene length, protein length | 264 bp, 88 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | flgN, yvyF |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 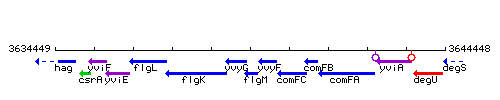
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed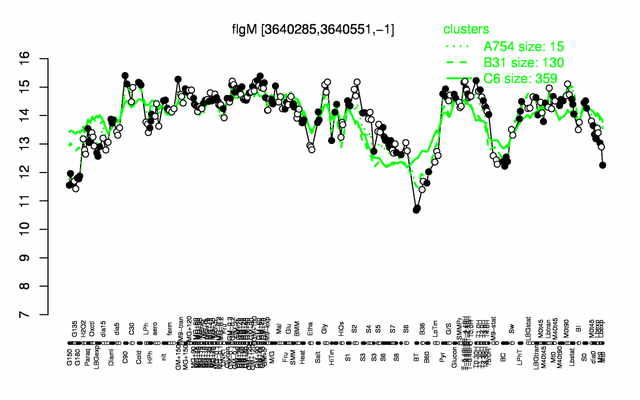
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
sigma factors and their control, motility and chemotaxis
This gene is a member of the following regulons
ComK regulon, DegU regulon, ScoC regulon, SigD regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35430
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35430
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: flgM family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35430
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39809
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Wai Kit Ma, Rachel Hendrix, Claire Stewart, Eric V Campbell, Mitchell Lavarias, Kolyn Morris, Shauna Nichol, Matthew J Gage
FlgM proteins from different bacteria exhibit different structural characteristics.
Biochim Biophys Acta: 2013, 1834(4);808-16
[PubMed:23352839]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Yi-Huang Hsueh, Loralyn M Cozy, Lok-To Sham, Rebecca A Calvo, Alina D Gutu, Malcolm E Winkler, Daniel B Kearns
DegU-phosphate activates expression of the anti-sigma factor FlgM in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 81(4);1092-108
[PubMed:21736639]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Loralyn M Cozy, Daniel B Kearns
Gene position in a long operon governs motility development in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 76(2);273-85
[PubMed:20233303]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Prashant Kodgire, K Krishnamurthy Rao
A dual mode of regulation of flgM by ScoC in Bacillus subtilis.
Can J Microbiol: 2009, 55(8);983-9
[PubMed:19898538]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
M G Bertero, B Gonzales, C Tarricone, F Ceciliani, A Galizzi
Overproduction and characterization of the Bacillus subtilis anti-sigma factor FlgM.
J Biol Chem: 1999, 274(17);12103-7
[PubMed:10207036]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Fredrick, J D Helmann
FlgM is a primary regulator of sigmaD activity, and its absence restores motility to a sinR mutant.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(23);7010-3
[PubMed:8955328]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Caramori, D Barilla, C Nessi, L Sacchi, A Galizzi
Role of FlgM in sigma D-dependent gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(11);3113-8
[PubMed:8655488]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D B Mirel, P Lauer, M J Chamberlin
Identification of flagellar synthesis regulatory and structural genes in a sigma D-dependent operon of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(15);4492-500
[PubMed:8045879]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J A Londoño-Vallejo, D Dubnau
comF, a Bacillus subtilis late competence locus, encodes a protein similar to ATP-dependent RNA/DNA helicases.
Mol Microbiol: 1993, 9(1);119-31
[PubMed:8412657]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)