Difference between revisions of "ClpC"
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
<div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | <div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" |'''[http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=clpC_103572_106004_1 Expression at a glance]'''   {{PubMed|22383849}}<br/>[[Image:clpC_expression.png|500px]] | + | |colspan="2" |'''[http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=clpC_103572_106004_1 Expression at a glance]'''   {{PubMed|22383849}}<br/>[[Image:clpC_expression.png|500px|link=http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/expression.php?search=BSU00860]] |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 12:20, 16 May 2013
- Description: ATPase subunit of the ATP-dependent ClpC-ClpP protease, involved in competence development, heat shock regulation, motility, sporulation, protein quality control, biofilm formation
| Gene name | clpC |
| Synonyms | mecB |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ATPase subunit of the ClpC-ClpP protease |
| Function | protein degradation positive regulator of autolysin (LytC and LytD) synthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: clpC | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: ClpC | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Stress | |
| MW, pI | 89 kDa, 5.746 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2430 bp, 810 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mcsB, radA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 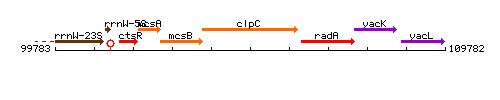
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed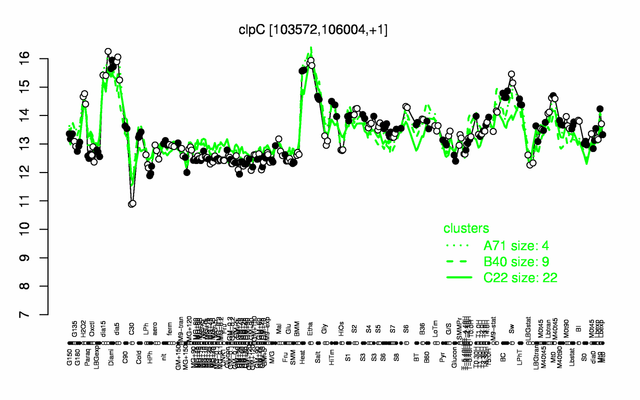
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
proteolysis, sporulation proteins, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB), heat shock proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CtsR regulon, SigB regulon, SigF regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00860
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
- A mutation was found in this gene after evolution under relaxed selection for sporulation PubMed
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATPase/chaperone
- Protein family: mecA family (according to Swiss-Prot) clpA/clpB family. ClpC subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot), AAA+ -type ATPase (IPR013093) InterPro (PF07724) PFAM
Targets of ClpC-ClpP-dependent protein degradation
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: AAA-ATPase PFAM
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on Arg-5 and Arg-254 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: P37571
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion: C-terminal GFP fusions (single copy, also as CFP and YFP variants) available from the Hamoen Lab
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Leendert Hamoen, Newcastle University, UK homepage
Kürsad Turgay, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Additional reviews: PubMed
Aurelia Battesti, Susan Gottesman
Roles of adaptor proteins in regulation of bacterial proteolysis.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2013, 16(2);140-7
[PubMed:23375660]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Dorte Frees, Kirsi Savijoki, Pekka Varmanen, Hanne Ingmer
Clp ATPases and ClpP proteolytic complexes regulate vital biological processes in low GC, Gram-positive bacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 63(5);1285-95
[PubMed:17302811]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original Publications
Additional publications: PubMed
Alexander K W Elsholz, Kürsad Turgay, Stephan Michalik, Bernd Hessling, Katrin Gronau, Dan Oertel, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
Global impact of protein arginine phosphorylation on the physiology of Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(19);7451-6
[PubMed:22517742]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christopher T Brown, Laura K Fishwick, Binna M Chokshi, Marissa A Cuff, Jay M Jackson, Travis Oglesby, Alison T Rioux, Enrique Rodriguez, Gregory S Stupp, Austin H Trupp, James S Woollcombe-Clarke, Tracy N Wright, William J Zaragoza, Jennifer C Drew, Eric W Triplett, Wayne L Nicholson
Whole-genome sequencing and phenotypic analysis of Bacillus subtilis mutants following evolution under conditions of relaxed selection for sporulation.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2011, 77(19);6867-77
[PubMed:21821766]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
A K W Elsholz, K Hempel, S Michalik, K Gronau, D Becher, M Hecker, U Gerth
Activity control of the ClpC adaptor McsB in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(15);3887-93
[PubMed:21622759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Feng Wang, Ziqing Mei, Yutao Qi, Chuangye Yan, Qi Hu, Jiawei Wang, Yigong Shi
Structure and mechanism of the hexameric MecA-ClpC molecular machine.
Nature: 2011, 471(7338);331-5
[PubMed:21368759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yunrong Chai, Roberto Kolter, Richard Losick
Reversal of an epigenetic switch governing cell chaining in Bacillus subtilis by protein instability.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 78(1);218-29
[PubMed:20923420]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alexander K W Elsholz, Stephan Michalik, Daniela Zühlke, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
CtsR, the Gram-positive master regulator of protein quality control, feels the heat.
EMBO J: 2010, 29(21);3621-9
[PubMed:20852588]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Mitsuo Ogura, Kensuke Tsukahara
Autoregulation of the Bacillus subtilis response regulator gene degU is coupled with the proteolysis of DegU-P by ClpCP.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 75(5);1244-59
[PubMed:20070525]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ziqing Mei, Feng Wang, Yutao Qi, Zhiyuan Zhou, Qi Hu, Han Li, Jiawei Wu, Yigong Shi
Molecular determinants of MecA as a degradation tag for the ClpCP protease.
J Biol Chem: 2009, 284(49);34366-75
[PubMed:19767395]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Douglas J Kojetin, Patrick D McLaughlin, Richele J Thompson, David Dubnau, Peter Prepiak, Mark Rance, John Cavanagh
Structural and motional contributions of the Bacillus subtilis ClpC N-domain to adaptor protein interactions.
J Mol Biol: 2009, 387(3);639-52
[PubMed:19361434]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jeanette Hahn, Naomi Kramer, Kenneth Briley, David Dubnau
McsA and B mediate the delocalization of competence proteins from the cell poles of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 72(1);202-15
[PubMed:19226326]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
James Kain, Gina G He, Richard Losick
Polar localization and compartmentalization of ClpP proteases during growth and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(20);6749-57
[PubMed:18689476]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lyle A Simmons, Alan D Grossman, Graham C Walker
Clp and Lon proteases occupy distinct subcellular positions in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(20);6758-68
[PubMed:18689473]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ulf Gerth, Holger Kock, Ilja Kusters, Stephan Michalik, Robert L Switzer, Michael Hecker
Clp-dependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(1);321-31
[PubMed:17981983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Peter Prepiak, David Dubnau
A peptide signal for adapter protein-mediated degradation by the AAA+ protease ClpCP.
Mol Cell: 2007, 26(5);639-47
[PubMed:17560370]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Stephanie T Wang, Barbara Setlow, Erin M Conlon, Jessica L Lyon, Daisuke Imamura, Tsutomu Sato, Peter Setlow, Richard Losick, Patrick Eichenberger
The forespore line of gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Biol: 2006, 358(1);16-37
[PubMed:16497325]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Holger Kock, Ulf Gerth, Michael Hecker
MurAA, catalysing the first committed step in peptidoglycan biosynthesis, is a target of Clp-dependent proteolysis in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 51(4);1087-102
[PubMed:14763982]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulf Gerth, Janine Kirstein, Jörg Mostertz, Torsten Waldminghaus, Marcus Miethke, Holger Kock, Michael Hecker
Fine-tuning in regulation of Clp protein content in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(1);179-91
[PubMed:14679237]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Qi Pan, Richard Losick
Unique degradation signal for ClpCP in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(17);5275-8
[PubMed:12923101]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Michiko M Nakano, Shunji Nakano, Peter Zuber
Spx (YjbD), a negative effector of competence in Bacillus subtilis, enhances ClpC-MecA-ComK interaction.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 44(5);1341-9
[PubMed:12028382]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Marjan Persuh, Ines Mandic-Mulec, David Dubnau
A MecA paralog, YpbH, binds ClpC, affecting both competence and sporulation.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(8);2310-3
[PubMed:11914365]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Turgay, M Persuh, J Hahn, D Dubnau
Roles of the two ClpC ATP binding sites in the regulation of competence and the stress response.
Mol Microbiol: 2001, 42(3);717-27
[PubMed:11722737]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Q Pan, D A Garsin, R Losick
Self-reinforcing activation of a cell-specific transcription factor by proteolysis of an anti-sigma factor in B. subtilis.
Mol Cell: 2001, 8(4);873-83
[PubMed:11684022]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Petersohn, M Brigulla, S Haas, J D Hoheisel, U Völker, M Hecker
Global analysis of the general stress response of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(19);5617-31
[PubMed:11544224]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Krüger, E Witt, S Ohlmeier, R Hanschke, M Hecker
The clp proteases of Bacillus subtilis are directly involved in degradation of misfolded proteins.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(11);3259-65
[PubMed:10809708]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Persuh, K Turgay, I Mandic-Mulec, D Dubnau
The N- and C-terminal domains of MecA recognize different partners in the competence molecular switch.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 33(4);886-94
[PubMed:10447896]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
I Derré, G Rapoport, T Msadek
CtsR, a novel regulator of stress and heat shock response, controls clp and molecular chaperone gene expression in gram-positive bacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 31(1);117-31
[PubMed:9987115]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Turgay, J Hahn, J Burghoorn, D Dubnau
Competence in Bacillus subtilis is controlled by regulated proteolysis of a transcription factor.
EMBO J: 1998, 17(22);6730-8
[PubMed:9890793]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
EIke Krüger, Tarek Msadek, Steffen Ohlmeier, Michael Hecker
The Bacillus subtilis clpC operon encodes DNA repair and competence proteins.
Microbiology (Reading): 1997, 143 ( Pt 4);1309-1316
[PubMed:9141693]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Turgay, L W Hamoen, G Venema, D Dubnau
Biochemical characterization of a molecular switch involving the heat shock protein ClpC, which controls the activity of ComK, the competence transcription factor of Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1997, 11(1);119-28
[PubMed:9000055]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Krüger, T Msadek, M Hecker
Alternate promoters direct stress-induced transcription of the Bacillus subtilis clpC operon.
Mol Microbiol: 1996, 20(4);713-23
[PubMed:8793870]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Kong, D Dubnau
Regulation of competence-specific gene expression by Mec-mediated protein-protein interaction in Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1994, 91(13);5793-7
[PubMed:8016067]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Msadek, F Kunst, G Rapoport
MecB of Bacillus subtilis, a member of the ClpC ATPase family, is a pleiotropic regulator controlling competence gene expression and growth at high temperature.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1994, 91(13);5788-92
[PubMed:8016066]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Krüger, U Völker, M Hecker
Stress induction of clpC in Bacillus subtilis and its involvement in stress tolerance.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(11);3360-7
[PubMed:8195092]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Roggiani, J Hahn, D Dubnau
Suppression of early competence mutations in Bacillus subtilis by mec mutations.
J Bacteriol: 1990, 172(7);4056-63
[PubMed:2113920]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)