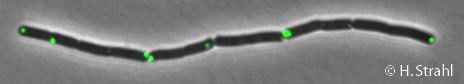
Difference between revisions of "ClpP"
(→Reviews) |
(→References) |
||
| Line 148: | Line 148: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | |||
==Reviews== | ==Reviews== | ||
'''Additional reviews:''' {{PubMed|19609260,19781636}} | '''Additional reviews:''' {{PubMed|19609260,19781636}} | ||
<pubmed> 16211032 17302811 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 16211032 17302811 </pubmed> | ||
| − | |||
==Original Publications== | ==Original Publications== | ||
'''Additional publications:''' {{PubMed|17380125,12598648,9890793,20049702,20049702}} | '''Additional publications:''' {{PubMed|17380125,12598648,9890793,20049702,20049702}} | ||
<pubmed>9643546,10809708,11807061,9987115,14679237,18689476,15317791,17586624,11684022,12923101,17560370, 16899079,19226326 , 20070525,9987115,11544224 14763982 9643546, 19767395 11112444 9535081 18689473 20305655 20852588 16200071 21969594 </pubmed> | <pubmed>9643546,10809708,11807061,9987115,14679237,18689476,15317791,17586624,11684022,12923101,17560370, 16899079,19226326 , 20070525,9987115,11544224 14763982 9643546, 19767395 11112444 9535081 18689473 20305655 20852588 16200071 21969594 </pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 09:40, 31 October 2011
- Description: ATP-dependent Clp protease proteolytic subunit (class III heat-shock protein)
| Gene name | clpP |
| Synonyms | yvdN |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ATP-dependent Clp protease proteolytic subunit |
| Function | protein degradation |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: ClpP | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Phosphorelay, Stress | |
| MW, pI | 21 kDa, 5.008 |
| Gene length, protein length | 591 bp, 197 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | trnQ-Arg, pgcM |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 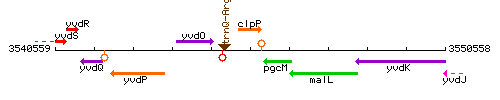
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
proteolysis, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB), heat shock proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU34540
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Hydrolysis of proteins to small peptides in the presence of ATP and magnesium (according to Swiss-Prot) endopeptidase/proteolysis
- Protein family: peptidase S14 family (according to Swiss-Prot) ClpP (IPR001907) InterPro, (PF00574) PFAM
- Paralogous protein(s):
Targets of ClpC-ClpP-dependent protein degradation
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: P80244
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 3.4.21.92
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: clpP PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- clpP::spec and clpP::cat, available in the Leendert Hamoen lab
- GP551 (spc), available in the Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion: C-terminal GFP fusions (both single copy and as 2th copy in amyE locus, also as CFP and YFP variants) available in the Leendert Hamoen lab
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Leendert Hamoen, Newcastle University, UK homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Additional reviews: PubMed
Original Publications
Additional publications: PubMed
Peter Sass, Michaele Josten, Kirsten Famulla, Guido Schiffer, Hans-Georg Sahl, Leendert Hamoen, Heike Brötz-Oesterhelt
Antibiotic acyldepsipeptides activate ClpP peptidase to degrade the cell division protein FtsZ.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2011, 108(42);17474-9
[PubMed:21969594]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alexander K W Elsholz, Stephan Michalik, Daniela Zühlke, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
CtsR, the Gram-positive master regulator of protein quality control, feels the heat.
EMBO J: 2010, 29(21);3621-9
[PubMed:20852588]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Byung-Gil Lee, Eun Young Park, Kyung-Eun Lee, Hyesung Jeon, Kwang Hoon Sung, Holger Paulsen, Helga Rübsamen-Schaeff, Heike Brötz-Oesterhelt, Hyun Kyu Song
Structures of ClpP in complex with acyldepsipeptide antibiotics reveal its activation mechanism.
Nat Struct Mol Biol: 2010, 17(4);471-8
[PubMed:20305655]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Mitsuo Ogura, Kensuke Tsukahara
Autoregulation of the Bacillus subtilis response regulator gene degU is coupled with the proteolysis of DegU-P by ClpCP.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 75(5);1244-59
[PubMed:20070525]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ziqing Mei, Feng Wang, Yutao Qi, Zhiyuan Zhou, Qi Hu, Han Li, Jiawei Wu, Yigong Shi
Molecular determinants of MecA as a degradation tag for the ClpCP protease.
J Biol Chem: 2009, 284(49);34366-75
[PubMed:19767395]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jeanette Hahn, Naomi Kramer, Kenneth Briley, David Dubnau
McsA and B mediate the delocalization of competence proteins from the cell poles of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 72(1);202-15
[PubMed:19226326]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
James Kain, Gina G He, Richard Losick
Polar localization and compartmentalization of ClpP proteases during growth and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(20);6749-57
[PubMed:18689476]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lyle A Simmons, Alan D Grossman, Graham C Walker
Clp and Lon proteases occupy distinct subcellular positions in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(20);6758-68
[PubMed:18689473]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Adam Reeves, Ulf Gerth, Uwe Völker, W G Haldenwang
ClpP modulates the activity of the Bacillus subtilis stress response transcription factor, sigmaB.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(17);6168-75
[PubMed:17586624]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Peter Prepiak, David Dubnau
A peptide signal for adapter protein-mediated degradation by the AAA+ protease ClpCP.
Mol Cell: 2007, 26(5);639-47
[PubMed:17560370]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Stephan Zellmeier, Wolfgang Schumann, Thomas Wiegert
Involvement of Clp protease activity in modulating the Bacillus subtilissigmaw stress response.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 61(6);1569-82
[PubMed:16899079]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Heike Brötz-Oesterhelt, Dieter Beyer, Hein-Peter Kroll, Rainer Endermann, Christoph Ladel, Werner Schroeder, Berthold Hinzen, Siegfried Raddatz, Holger Paulsen, Kerstin Henninger, Julia E Bandow, Hans-Georg Sahl, Harald Labischinski
Dysregulation of bacterial proteolytic machinery by a new class of antibiotics.
Nat Med: 2005, 11(10);1082-7
[PubMed:16200071]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Holger Kock, Ulf Gerth, Michael Hecker
The ClpP peptidase is the major determinant of bulk protein turnover in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(17);5856-64
[PubMed:15317791]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Holger Kock, Ulf Gerth, Michael Hecker
MurAA, catalysing the first committed step in peptidoglycan biosynthesis, is a target of Clp-dependent proteolysis in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 51(4);1087-102
[PubMed:14763982]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulf Gerth, Janine Kirstein, Jörg Mostertz, Torsten Waldminghaus, Marcus Miethke, Holger Kock, Michael Hecker
Fine-tuning in regulation of Clp protein content in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(1);179-91
[PubMed:14679237]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Qi Pan, Richard Losick
Unique degradation signal for ClpCP in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(17);5275-8
[PubMed:12923101]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Tiina Pummi, Soile Leskelä, Eva Wahlström, Ulf Gerth, Harold Tjalsma, Michael Hecker, Matti Sarvas, Vesa P Kontinen
ClpXP protease regulates the signal peptide cleavage of secretory preproteins in Bacillus subtilis with a mechanism distinct from that of the Ecs ABC transporter.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(4);1010-8
[PubMed:11807061]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Q Pan, D A Garsin, R Losick
Self-reinforcing activation of a cell-specific transcription factor by proteolysis of an anti-sigma factor in B. subtilis.
Mol Cell: 2001, 8(4);873-83
[PubMed:11684022]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Petersohn, M Brigulla, S Haas, J D Hoheisel, U Völker, M Hecker
Global analysis of the general stress response of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(19);5617-31
[PubMed:11544224]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Nanamiya, K Takahashi, M Fujita, F Kawamura
Deficiency of the initiation events of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis clpP mutant can be suppressed by a lack of the Spo0E protein phosphatase.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun: 2000, 279(1);229-33
[PubMed:11112444]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Krüger, E Witt, S Ohlmeier, R Hanschke, M Hecker
The clp proteases of Bacillus subtilis are directly involved in degradation of misfolded proteins.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(11);3259-65
[PubMed:10809708]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
I Derré, G Rapoport, T Msadek
CtsR, a novel regulator of stress and heat shock response, controls clp and molecular chaperone gene expression in gram-positive bacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 1999, 31(1);117-31
[PubMed:9987115]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
U Gerth, E Krüger, I Derré, T Msadek, M Hecker
Stress induction of the Bacillus subtilis clpP gene encoding a homologue of the proteolytic component of the Clp protease and the involvement of ClpP and ClpX in stress tolerance.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 28(4);787-802
[PubMed:9643546]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Msadek, V Dartois, F Kunst, M L Herbaud, F Denizot, G Rapoport
ClpP of Bacillus subtilis is required for competence development, motility, degradative enzyme synthesis, growth at high temperature and sporulation.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 27(5);899-914
[PubMed:9535081]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)