Difference between revisions of "DivIC"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[cell division]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[sporulation proteins]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, W, X, Y)]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[essential genes]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[membrane proteins]]}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[SigE regulon]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[SigM regulon]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[SigW regulon]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[SigX regulon]]}} | ||
=The gene= | =The gene= | ||
| Line 51: | Line 64: | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=The protein= | =The protein= | ||
Revision as of 15:16, 8 December 2010
- Description: cell-division initiation protein (septum formation), component of septosome (with DivIB)
| Gene name | divIC |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | cell-division protein |
| Function | septum formation |
| MW, pI | 14 kDa, 9.968 |
| Gene length, protein length | 375 bp, 125 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yabQ, yabR |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 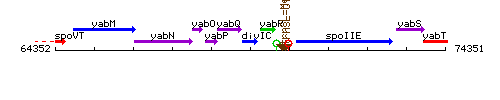
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, sporulation proteins, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, W, X, Y), essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
SigE regulon, SigM regulon, SigW regulon, SigX regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00620
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: membrane bound PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P37471
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information: there are about 50,000 molecules of DivIC per cell PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Inga Wadenpohl, Marc Bramkamp
DivIC stabilizes FtsL against RasP cleavage.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(19);5260-3
[PubMed:20644139]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Warawan Eiamphungporn, John D Helmann
The Bacillus subtilis sigma(M) regulon and its contribution to cell envelope stress responses.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 67(4);830-48
[PubMed:18179421]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Richard A Daniel, Marie-Françoise Noirot-Gros, Philippe Noirot, Jeff Errington
Multiple interactions between the transmembrane division proteins of Bacillus subtilis and the role of FtsL instability in divisome assembly.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(21);7396-404
[PubMed:16936019]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Scott A Robson, Katharine A Michie, Joel P Mackay, Elizabeth Harry, Glenn F King
The Bacillus subtilis cell division proteins FtsL and DivIC are intrinsically unstable and do not interact with one another in the absence of other septasomal components.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 44(3);663-74
[PubMed:11994149]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Kei Asai, Hiromu Takamatsu, Megumi Iwano, Takeko Kodama, Kazuhito Watabe, Naotake Ogasawara
The Bacillus subtilis yabQ gene is essential for formation of the spore cortex.
Microbiology (Reading): 2001, 147(Pt 4);919-927
[PubMed:11283287]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
V L Katis, R G Wake, E J Harry
Septal localization of the membrane-bound division proteins of Bacillus subtilis DivIB and DivIC is codependent only at high temperatures and requires FtsZ.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(12);3607-11
[PubMed:10852898]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J Sievers, J Errington
The Bacillus subtilis cell division protein FtsL localizes to sites of septation and interacts with DivIC.
Mol Microbiol: 2000, 36(4);846-55
[PubMed:10844672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N King, O Dreesen, P Stragier, K Pogliano, R Losick
Septation, dephosphorylation, and the activation of sigmaF during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1999, 13(9);1156-67
[PubMed:10323866]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
V L Katis, R G Wake
Membrane-bound division proteins DivIB and DivIC of Bacillus subtilis function solely through their external domains in both vegetative and sporulation division.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(9);2710-8
[PubMed:10217758]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R A Daniel, E J Harry, V L Katis, R G Wake, J Errington
Characterization of the essential cell division gene ftsL(yIID) of Bacillus subtilis and its role in the assembly of the division apparatus.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 29(2);593-604
[PubMed:9720875]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
V L Katis, E J Harry, R G Wake
The Bacillus subtilis division protein DivIC is a highly abundant membrane-bound protein that localizes to the division site.
Mol Microbiol: 1997, 26(5);1047-55
[PubMed:9426141]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P A Levin, R Losick
Characterization of a cell division gene from Bacillus subtilis that is required for vegetative and sporulation septum formation.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(5);1451-9
[PubMed:8113187]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Additional publications: PubMed