Difference between revisions of "CtsR"
(→Reviews) |
|||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
==Reviews== | ==Reviews== | ||
| − | <pubmed>14984053 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>14984053 21078442 </pubmed> |
| + | |||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
<pubmed>8793870, 9987115,12923084,11717291,16788169,11069659, 9852015,12884008,8195092,9987115,11544224 9852015, 11179229, 8793870 , 12884008 20852588 </pubmed> | <pubmed>8793870, 9987115,12923084,11717291,16788169,11069659, 9852015,12884008,8195092,9987115,11544224 9852015, 11179229, 8793870 , 12884008 20852588 </pubmed> | ||
Revision as of 19:26, 18 November 2010
| Gene name | ctsR |
| Synonyms | yacG |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcription repressor |
| Function | regulation of protein degradation |
| Regulatory function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Stress, Phosphorelay | |
| MW, pI | 17 kDa, 9.261 |
| Gene length, protein length | 462 bp, 154 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | rrnW-5S, mcsA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 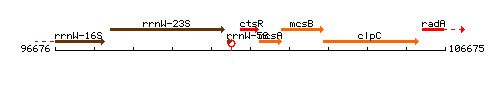
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00830
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ctsR family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- UniProt: P37568
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information: the mRNA is very stable (half-life > 15 min) PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Alexander K W Elsholz, Ulf Gerth, Michael Hecker
Regulation of CtsR activity in low GC, Gram+ bacteria.
Adv Microb Physiol: 2010, 57;119-44
[PubMed:21078442]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Wolfgang Schumann
The Bacillus subtilis heat shock stimulon.
Cell Stress Chaperones: 2003, 8(3);207-17
[PubMed:14984053]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications
Additional publications: PubMed