GuaB
- Description: IMP dehydrogenase
| Gene name | guaB |
| Synonyms | guaA |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | IMP dehydrogenase |
| Function | biosynthesis of GMP |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: GuaB | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: guaB | |
| MW, pI | 52 kDa, 6.168 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1464 bp, 488 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yaaC, dacA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 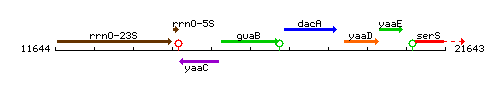
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed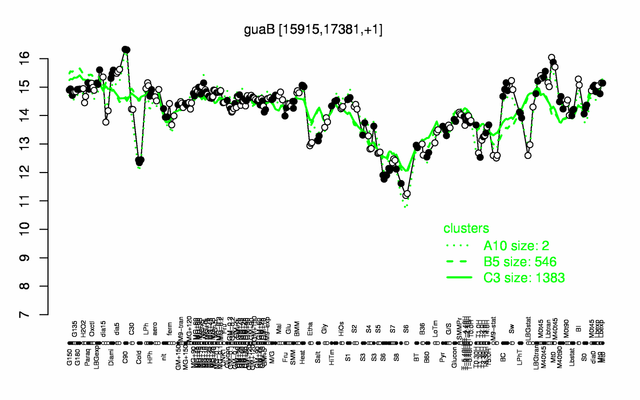
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of nucleotides, essential genes, phosphoproteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00090
Phenotypes of a mutant
- essential PubMed
- reduced expression of guaB suppresses the requirement of a relA sasA sasB triple mutant for branched chain amino acids, methionine and threonine PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00090
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD+ + H2O = xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: IMPDH/GMPR family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- inhibition of enzymatic activity by (p)ppGpp during the ´stringent response´PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00090
- Structure: 1VRD (from Thermotoga maritima msb8, 60% identity, 80% similarity)
- UniProt: P21879
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.1.1.205
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: guaB PubMed
- Additional information:
- the mRNA is very stable (half-life > 15 min) PubMed
- inhibition of enzymatic activity by (p)ppGpp during the ´stringent response´PubMed
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 3210 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 20338 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 6450 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 4621 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 5993 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Alycia N Bittner, Allison Kriel, Jue D Wang
Lowering GTP level increases survival of amino acid starvation but slows growth rate for Bacillus subtilis cells lacking (p)ppGpp.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(11);2067-76
[PubMed:24682323]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Allison Kriel, Shaun R Brinsmade, Jessica L Tse, Ashley K Tehranchi, Alycia N Bittner, Abraham L Sonenshein, Jue D Wang
GTP dysregulation in Bacillus subtilis cells lacking (p)ppGpp results in phenotypic amino acid auxotrophy and failure to adapt to nutrient downshift and regulate biosynthesis genes.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(1);189-201
[PubMed:24163341]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Allison Kriel, Alycia N Bittner, Sok Ho Kim, Kuanqing Liu, Ashley K Tehranchi, Winnie Y Zou, Samantha Rendon, Rui Chen, Benjamin P Tu, Jue D Wang
Direct regulation of GTP homeostasis by (p)ppGpp: a critical component of viability and stress resistance.
Mol Cell: 2012, 48(2);231-41
[PubMed:22981860]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Bui Khanh Chi, Alexandra A Roberts, Tran Thi Thanh Huyen, Katrin Bäsell, Dörte Becher, Dirk Albrecht, Chris J Hamilton, Haike Antelmann
S-bacillithiolation protects conserved and essential proteins against hypochlorite stress in firmicutes bacteria.
Antioxid Redox Signal: 2013, 18(11);1273-95
[PubMed:22938038]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Eymann, Dörte Becher, Jörg Bernhardt, Katrin Gronau, Anja Klutzny, Michael Hecker
Dynamics of protein phosphorylation on Ser/Thr/Tyr in Bacillus subtilis.
Proteomics: 2007, 7(19);3509-26
[PubMed:17726680]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Falko Hochgräfe, Jörg Mostertz, Dierk-Christoph Pöther, Dörte Becher, John D Helmann, Michael Hecker
S-cysteinylation is a general mechanism for thiol protection of Bacillus subtilis proteins after oxidative stress.
J Biol Chem: 2007, 282(36);25981-5
[PubMed:17611193]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Hambraeus, C von Wachenfeldt, L Hederstedt
Genome-wide survey of mRNA half-lives in Bacillus subtilis identifies extremely stable mRNAs.
Mol Genet Genomics: 2003, 269(5);706-14
[PubMed:12884008]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Yoshiko Nakaura, Robert P Shivers, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Richard Losick, Yasutaro Fujita, Abraham L Sonenshein
Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(6);1911-22
[PubMed:12618455]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H H Saxild, P Nygaard
Regulation of levels of purine biosynthetic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: effects of changing purine nucleotide pools.
J Gen Microbiol: 1991, 137(10);2387-94
[PubMed:1722815]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J M Lopez, A Dromerick, E Freese
Response of guanosine 5'-triphosphate concentration to nutritional changes and its significance for Bacillus subtilis sporulation.
J Bacteriol: 1981, 146(2);605-13
[PubMed:6111556]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)