PhoR
- Description: two-component sensor kinase, regulation of phosphate metabolism
| Gene name | phoR |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component sensor kinase |
| Function | regulation of phosphate metabolism |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: phoR | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: PhoR | |
| MW, pI | 64 kDa, 5.957 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1737 bp, 579 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | polA, phoP |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 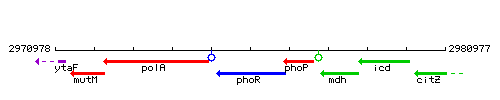
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed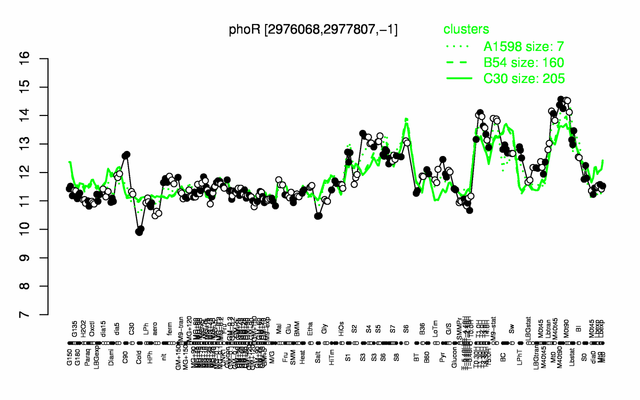
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
phosphate metabolism, protein modification, transcription factors and their control, sporulation proteins, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB), membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CcpA regulon, PhoP regulon, SigB regulon, SigE regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29100
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29100
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: autophosphorylation, phosphorylation of PhoP
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- two transmembrane segments
- PAS domain, for binding of an intermediate of wall teichoic acid biosynthesis PubMed
- C-terminal histidine phosphotransferase domain
- Modification:
- autophosphorylation on a His residue in response to the the availability of an intermediate of wall teichoic acid bioynthesis, autophosphorylation is prevented by binding of this intermediate to the intracellular PAS domain of PhoR PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- activity is inhibited by binding of an intermediate of wall teichoic acid biosynthesis to the intracellular PAS domain of PhoR PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29100
- UniProt: P23545
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 453 PubMed
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Marion Hulett, University of Illinois at Chicago, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Georg Fritz, Thorsten Mascher
A balancing act times two: sensing and regulating cell envelope homeostasis in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2014, 94(6);1201-7
[PubMed:25355628]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
C Fabret, V A Feher, J A Hoch
Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(7);1975-83
[PubMed:10094672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications