GlmS
Revision as of 14:07, 17 April 2014 by 134.76.70.252 (talk)
- Description: glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase
| Gene name | glmS |
| Synonyms | gcaA, ybxD |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase |
| Function | cell wall synthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: glmS | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: glmS | |
| MW, pI | 65 kDa, 4.796 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1800 bp, 600 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | glmM, alkA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 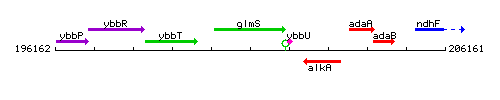
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, biosynthesis of cell wall components, essential genes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU01780
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU01780
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: L-glutamine + D-fructose 6-phosphate = L-glutamate + D-glucosamine 6-phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU01780
- UniProt: P39754
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 2.6.1.16
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism: glmS ribozyme: glucosamine 6-phosphate binds the leader mRNA, and a riboswitch with ribozyme activity cleaves off the glmS section from the mRNA, resulting in stopp of transcript elongation
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- A ncRNA is predicted between glmM and glmS PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 340 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 2741 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1114 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 808 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 434 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Wade Winkler, University of Texas, USA, Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Philippe Durand, Béatrice Golinelli-Pimpaneau, Stéphane Mouilleron, Bernard Badet, Marie-Ange Badet-Denisot
Highlights of glucosamine-6P synthase catalysis.
Arch Biochem Biophys: 2008, 474(2);302-17
[PubMed:18279655]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
The glmS Ribozyme
Other Original Publications