Spx
- Description: transcriptional regulator Spx, involved in regulation of many genes, important for the prevention of protein aggregation during severe heat stress, required for protection against paraquat stress
| Gene name | spx |
| Synonyms | yjbD |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional regulator Spx |
| Function | negative and positive regulator of many genes |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: spx | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: Spx | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: spx | |
| MW, pI | 15,5 kDa, 7.80 |
| Gene length, protein length | 393 bp, 131 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | yjbC, yjbE |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 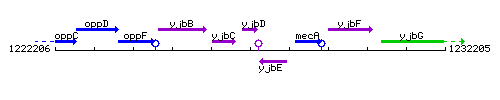
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed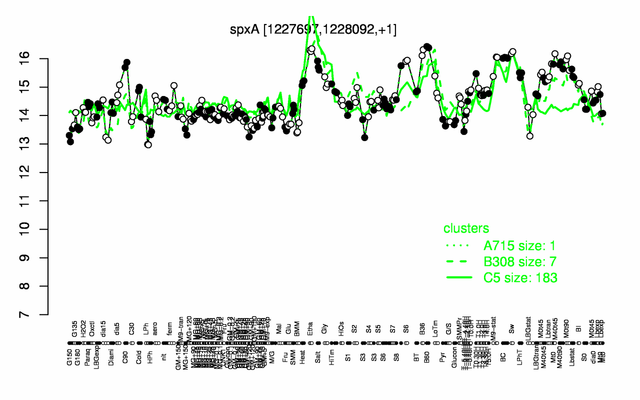
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB), cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), resistance against oxidative and electrophile stress,
This gene is a member of the following regulons
PerR regulon, SigB regulon, SigM regulon, SigW regulon, SigX regulon
The Spx regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU11500
Phenotypes of a mutant
- Loss of up-regulation of the methionine sulfoxide reductase (msrA-msrB) operon in response to thiol specific oxidative stress, also loss of trxA and trxB upregulation in response to thiol specific oxidative stress.
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: link
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- transcriptional regulator of many genes in response to thiol specific oxidative stress (transcription activator of trxA and trxB)
- in addition, Spx inhibits transcription by binding to the C-terminal domain of the alpha subunit of RNAP (RpoA), disrupting complex formation between RNAP and certain transcriptional activator proteins like ResD and ComA
- in response to thiol specific oxidative stress, Spx can also activate transcription, making it a general regulator that exerts both positive and negative control over transcription initiation
- involved in competence regulation PubMed
- Protein family: Spx subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot) Arsenate Reductase (ArsC) family, Spx subfamily
- Paralogous protein(s): MgsR
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: CXXC (10-13): Acts as a disulfide switch for the redox-sensitive transcriptional regulation of genes that function in thiol homeostasis.
- Modification: Cysteine oxidation of the CXXC motif
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- UniProt: O31602
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
- post-translational control by ClpX-ClpP: Spx naturally contains a C-terminal sequence that resembles the SsrA tag and targets the protein for degradation. PubMed
- proteolysis is enhanced by YjbH PubMed and counter-acted by YirB PubMed
- the mRNA is substantially stabilized upon depletion of RNase Y (the half-life of the monocistronic spx mRNA increases from 1 to 6 min) PubMed
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Peter Zuber, Oregon Health and Science University, USA Homepage
Richard Brennan, Houston, Texas, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
The Spx regulon
Tatiana Rochat, Pierre Nicolas, Olivier Delumeau, Alžbeta Rabatinová, Jana Korelusová, Aurélie Leduc, Philippe Bessières, Etienne Dervyn, Libor Krásny, Philippe Noirot
Genome-wide identification of genes directly regulated by the pleiotropic transcription factor Spx in Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2012, 40(19);9571-83
[PubMed:22904090]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kyle N Erwin, Shunji Nakano, Peter Zuber
Sulfate-dependent repression of genes that function in organosulfur metabolism in Bacillus subtilis requires Spx.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(12);4042-9
[PubMed:15937167]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Peter Zuber
Spx-RNA polymerase interaction and global transcriptional control during oxidative stress.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(7);1911-8
[PubMed:15028674]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Shunji Nakano, Elke Küster-Schöck, Alan D Grossman, Peter Zuber
Spx-dependent global transcriptional control is induced by thiol-specific oxidative stress in Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2003, 100(23);13603-8
[PubMed:14597697]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Structural analysis of Spx
Ann A Lin, Don Walthers, Peter Zuber
Residue substitutions near the redox center of Bacillus subtilis Spx affect RNA polymerase interaction, redox control, and Spx-DNA contact at a conserved cis-acting element.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(17);3967-78
[PubMed:23813734]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Valerie Lamour, Lars F Westblade, Elizabeth A Campbell, Seth A Darst
Crystal structure of the in vivo-assembled Bacillus subtilis Spx/RNA polymerase alpha subunit C-terminal domain complex.
J Struct Biol: 2009, 168(2);352-6
[PubMed:19580872]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kate J Newberry, Shunji Nakano, Peter Zuber, Richard G Brennan
Crystal structure of the Bacillus subtilis anti-alpha, global transcriptional regulator, Spx, in complex with the alpha C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2005, 102(44);15839-44
[PubMed:16249335]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original Publications