LcfB
- Description: long-chain fatty-acid-CoA ligase, involved in surfactin production
| Gene name | lcfB |
| Synonyms | yhfL |
| Essential | no |
| Product | long-chain fatty-acid-CoA ligase |
| Function | fatty acid degradation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: lcfB | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Fatty acid degradation | |
| MW, pI | 56 kDa, 5.301 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1539 bp, 513 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yhfK, yhfM |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 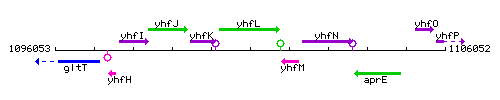
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed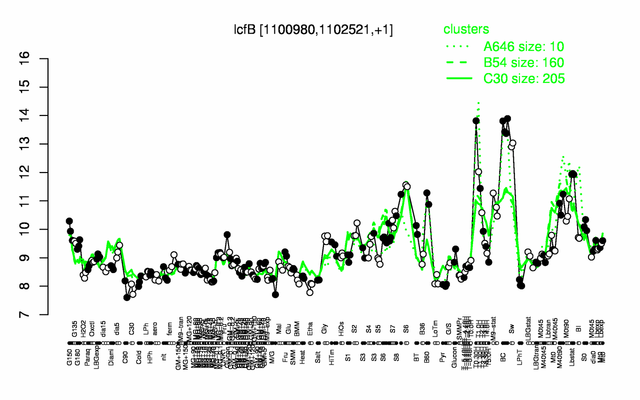
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU10270
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + a long-chain carboxylic acid + CoA = AMP + diphosphate + an acyl-CoA (according to Swiss-Prot), activates 3-hydroxy fatty acids for surfactin biosynthesis PubMed
- Protein family: ATP-dependent AMP-binding enzyme family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O07610
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 6.2.1.3
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: lcfB PubMed
- Regulation:
- induced in the presence of long-chain fatty acids (FadR) PubMed
- subject to carbon catabolite repression (CcpA-HPr(Ser-P) PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- FadR: transcription repression PubMed
- CcpA-HPr(Ser-P): transcription repression PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: available in Mohamed Marahiel's lab PubMed
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Femke I Kraas, Verena Helmetag, Melanie Wittmann, Matthias Strieker, Mohamed A Marahiel
Functional dissection of surfactin synthetase initiation module reveals insights into the mechanism of lipoinitiation.
Chem Biol: 2010, 17(8);872-80
[PubMed:20797616]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yasutaro Fujita, Hiroshi Matsuoka, Kazutake Hirooka
Regulation of fatty acid metabolism in bacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 66(4);829-39
[PubMed:17919287]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hiroshi Matsuoka, Kazutake Hirooka, Yasutaro Fujita
Organization and function of the YsiA regulon of Bacillus subtilis involved in fatty acid degradation.
J Biol Chem: 2007, 282(8);5180-94
[PubMed:17189250]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)