ScpA
- Description: DNA segregation and condensation protein
| Gene name | scpA |
| Synonyms | ypuG |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | DNA segregation and condensation protein |
| Function | maintenance of chromosome structure |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: scpA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: ScpA | |
| MW, pI | 29 kDa, 4.788 |
| Gene length, protein length | 753 bp, 251 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | scpB, ypuF |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 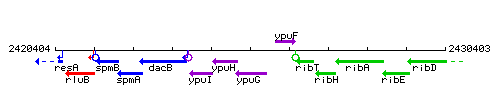
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed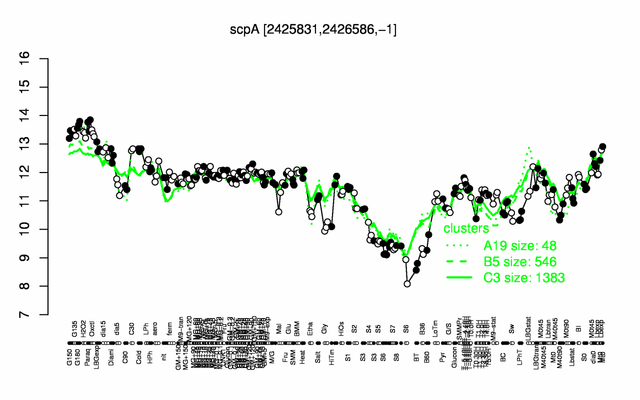
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
DNA condensation/ segregation, essential genes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU23220
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: scpA family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- nucleoid (Multiple) PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P35154
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Luise A K Kleine Borgmann, Hanna Hummel, Maximilian H Ulbrich, Peter L Graumann
SMC condensation centers in Bacillus subtilis are dynamic structures.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(10);2136-45
[PubMed:23475963]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Frank Bürmann, Ho-Chul Shin, Jérôme Basquin, Young-Min Soh, Victor Giménez-Oya, Yeon-Gil Kim, Byung-Ha Oh, Stephan Gruber
An asymmetric SMC-kleisin bridge in prokaryotic condensin.
Nat Struct Mol Biol: 2013, 20(3);371-9
[PubMed:23353789]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Stephan Gruber, Jeff Errington
Recruitment of condensin to replication origin regions by ParB/SpoOJ promotes chromosome segregation in B. subtilis.
Cell: 2009, 137(4);685-96
[PubMed:19450516]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jean-Christophe Meile, Ling Juan Wu, S Dusko Ehrlich, Jeff Errington, Philippe Noirot
Systematic localisation of proteins fused to the green fluorescent protein in Bacillus subtilis: identification of new proteins at the DNA replication factory.
Proteomics: 2006, 6(7);2135-46
[PubMed:16479537]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Etienne Dervyn, Marie-Françoise Noirot-Gros, Peggy Mervelet, Steven McGovern, S Dusko Ehrlich, Patrice Polard, Philippe Noirot
The bacterial condensin/cohesin-like protein complex acts in DNA repair and regulation of gene expression.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 51(6);1629-40
[PubMed:15009890]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Janet C Lindow, Masayoshi Kuwano, Shigeki Moriya, Alan D Grossman
Subcellular localization of the Bacillus subtilis structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) protein.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 46(4);997-1009
[PubMed:12421306]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jörg Soppa, Kazuo Kobayashi, Marie-Françoise Noirot-Gros, Dieter Oesterhelt, S Dusko Ehrlich, Etienne Dervyn, Naotake Ogasawara, Shigeki Moriya
Discovery of two novel families of proteins that are proposed to interact with prokaryotic SMC proteins, and characterization of the Bacillus subtilis family members ScpA and ScpB.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 45(1);59-71
[PubMed:12100548]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Judita Mascarenhas, Jörg Soppa, Alexander V Strunnikov, Peter L Graumann
Cell cycle-dependent localization of two novel prokaryotic chromosome segregation and condensation proteins in Bacillus subtilis that interact with SMC protein.
EMBO J: 2002, 21(12);3108-18
[PubMed:12065423]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Michael Hecker
Bacillus subtilis functional genomics: global characterization of the stringent response by proteome and transcriptome analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(9);2500-20
[PubMed:11948165]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
V Azevedo, A Sorokin, S D Ehrlich, P Serror
The transcriptional organization of the Bacillus subtilis 168 chromosome region between the spoVAF and serA genetic loci.
Mol Microbiol: 1993, 10(2);397-405
[PubMed:7934830]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)