GtaB
- Description: UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase, general stress protein
| Gene name | gtaB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase |
| Function | biosynthesis of teichoic acid |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: gtaB | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Lipid synthesis | |
| MW, pI | 32 kDa, 4.913 |
| Gene length, protein length | 876 bp, 292 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mnaA, yvzH |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 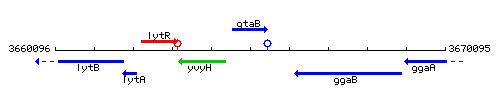
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed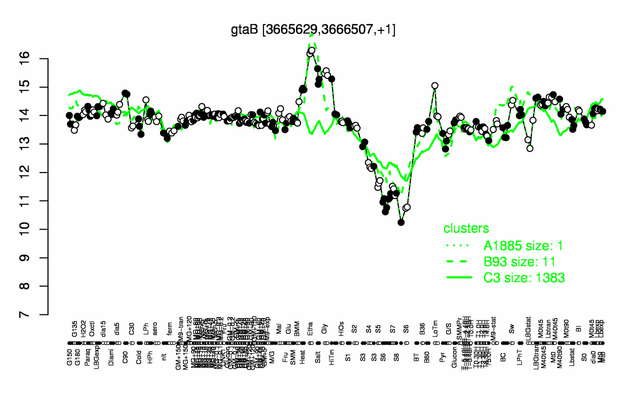
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, lipid metabolism/ other, biosynthesis of cell wall components, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB), phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35670
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: UTP + alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate = diphosphate + UDP-glucose (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: UDPGP type 2 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: Q05852
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.7.9
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: gtaB PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Alexander K W Elsholz, Kürsad Turgay, Stephan Michalik, Bernd Hessling, Katrin Gronau, Dan Oertel, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
Global impact of protein arginine phosphorylation on the physiology of Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(19);7451-6
[PubMed:22517742]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alain Lévine, Françoise Vannier, Cédric Absalon, Lauriane Kuhn, Peter Jackson, Elaine Scrivener, Valérie Labas, Joëlle Vinh, Patrick Courtney, Jérôme Garin, Simone J Séror
Analysis of the dynamic Bacillus subtilis Ser/Thr/Tyr phosphoproteome implicated in a wide variety of cellular processes.
Proteomics: 2006, 6(7);2157-73
[PubMed:16493705]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Petersohn, M Brigulla, S Haas, J D Hoheisel, U Völker, M Hecker
Global analysis of the general stress response of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(19);5617-31
[PubMed:11544224]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D Varón, S A Boylan, K Okamoto, C W Price
Bacillus subtilis gtaB encodes UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and is controlled by stationary-phase transcription factor sigma B.
J Bacteriol: 1993, 175(13);3964-71
[PubMed:8320212]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H M Pooley, D Paschoud, D Karamata
The gtaB marker in Bacillus subtilis 168 is associated with a deficiency in UDPglucose pyrophosphorylase.
J Gen Microbiol: 1987, 133(12);3481-93
[PubMed:2846750]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)