NatA
- Description: Na+ ABC transporter (export) (ATP-binding protein)
| Gene name | natA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | Na+ ABC transporter (export) (ATP-binding protein) |
| Function | sodium export |
| MW, pI | 27 kDa, 8.799 |
| Gene length, protein length | 738 bp, 246 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | natR, natB |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 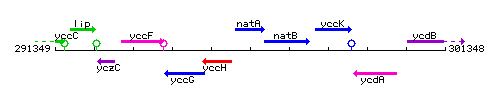
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU02750
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ABC transporter domain (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P46903
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Mitsuo Ogura, Kensuke Tsukahara, Kentaro Hayashi, Teruo Tanaka
The Bacillus subtilis NatK-NatR two-component system regulates expression of the natAB operon encoding an ABC transporter for sodium ion extrusion.
Microbiology (Reading): 2007, 153(Pt 3);667-675
[PubMed:17322186]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Quentin, G Fichant, F Denizot
Inventory, assembly and analysis of Bacillus subtilis ABC transport systems.
J Mol Biol: 1999, 287(3);467-84
[PubMed:10092453]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J Cheng, A A Guffanti, T A Krulwich
A two-gene ABC-type transport system that extrudes Na+ in Bacillus subtilis is induced by ethanol or protonophore.
Mol Microbiol: 1997, 23(6);1107-20
[PubMed:9106203]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)