Sandbox
- Description: Transcriptional antiterminator, controls expression of the ptsGHI operon
| Gene name | glcT |
| Synonyms | ykwA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional antiterminator of the ptsGHI operon |
| Function | transcriptional antiterminator |
| MW, pI | 33,0 kDa, 7.01 |
| Gene length, protein length | 855 bp, 285 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | ykvZ, ptsG |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 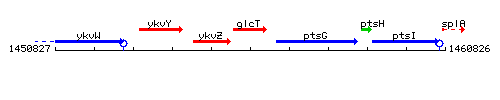
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU13880
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: transcriptional antiterminator, RNA-binding protein, binds the ptsG RAT sequence
- Protein family: antiterminator of the BglG/ SacY family
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- RNA-binding domain (N-terminal, constitutive antiterminator)
- 2x PTS regulation domains (PRDs) (C-terminal, neg. regulated by PtsG)
- Modification: phosphorylation (His104)
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry: [2]
- KEGG entry: [3]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP109 (in frame deletion), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector: pGP124 (full length, in pWH844), pGP114 (amino acids 1-60, RNA-binding domain, in pWH844), pGP230 (amino acids 1-60, RNA-binding domain with thrombin cleavage site, in pWH844), pGP164 (both PRDs, in pWH844), in addition diverse expression vectors for phosphorylation site mutants and for RBD mutants (all in pWH844), pGP424 (PRDI, in pWH844), pGP425 (PRDII, in pWH844), pGP442 (PRDI, in pGP570, with thrombin cleavage site), pGP443 (PRDII, in pGP570, with thrombin cleavage site), pGP575 (amino acids 1-60, RNA-binding domain with Strep-tag, in pGP574), all available in Stülke lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
- Stülke J, Martin-Verstraete I, Zagorec M (1997) Induction of the Bacillus subtilis ptsGHI operon by glucose is controlled by a novel antiterminator, GlcT Mol Microbiol. 25: 65-78. PubMed
- Bachem S, Stülke J. (1998) Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis GlcT antiterminator protein by components of the phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 180: 5319-26 PubMed
- Greenberg, D. B., Stülke, J. & Saier Jr., M. H. (2002) Domain analysis of transcriptional regulators bearing PTS-regulatory domains. Res. Microbiol. 153: 519-526. PubMed
- Langbein, I., Bachem, S. & Stülke, J. (1999) Specific interaction of the RNA binding domain of the Bacillus subtilis transcriptional antiterminator GlcT with its RNA target, RAT. J. Mol. Biol. 293: 795-805. PubMed
- Schilling, O., Herzberg, C., Hertrich, T., Vörsmann, H., Jessen, D., Hübner, S., Titgemeyer, F. & Stülke, J. (2006) Keeping signals straight in transcription regulation: specificity determinants for the interaction of a family of conserved bacterial RNA-protein couples. Nucl. Acids Res. 34: 6102-6115. PubMed
- Schilling, O., Langbein, I., Müller, M., Schmalisch, M. & Stülke, J. (2004) A protein-dependent riboswitch controlling ptsGHI operon expression in Bacillus subtilis: RNA structure rather than sequence provides interaction specificity. Nucl. Acids Res. 32: 2853-2864. PubMed
- Schmalisch, M., Bachem, S. & Stülke, J. (2003) Control of the Bacillus subtilis antiterminator protein GlcT by phosphorylation: Elucidation of the phosphorylation chain leading to inactivation of GlcT. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 51108-51115. PubMed
- Stülke, J., Arnaud, M., Rapoport, G., & Martin-Verstraete, I. (1998) PRD - A protein domain involved in PTS-dependent induction and carbon catabolite repression of catabolic operons in bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 28: 865-874. PubMed