Pgi
- Description: glucose 6-phosphate isomerase, glycolytic/ gluconeogenic enzyme
| Gene name | pgi |
| Synonyms | yugL |
| Essential | no |
| Product | glucose-6-phosphate isomerase |
| Function | enzyme in glycolysis/ gluconeogenesis |
| MW, pI | 50.4 kDa, 4.85 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1353 bp, 451 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | yugM, yugK |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) corrected | Protein sequence |
| Caution: The sequence for this gene in SubtiList contains errors | |
Genetic context 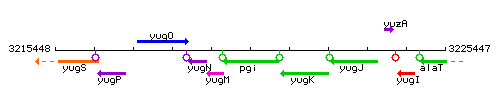
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates: 3219772 - 3221124
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: D-glucose 6-phosphate = D-fructose 6-phosphate
- Protein family: GPI family
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation on Thr-39 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: inhibited by 6-phosphogluconate (in B.caldotenax, B.stearothermophilus) PubMed
- Interactions:
- Localization: cytoplasm
Database entries
- Swiss prot entry: [3]
- KEGG entry: [4]
- E.C. number: [5]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: pgi PubMed
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation: constitutively expressed PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP508 (spc), available in Stülke lab
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
- Macek et al. (2007) The serine/ threonine/ tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 6: 697-707 PubMed
- Lee et al. (2008) Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic study of the phosphoglucose isomerase from Bacillus subtilis. Acta Cryst. Sect. F 64:1181-1183. PubMed
- Lin and Prasad (1975) Selection of a mutant of Bacillus subtilis deficient in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoglucoisomerase. J. Gen. Microbiol. 83:419-421. PubMed
- Ludwig, H., Homuth, G., Schmalisch, M., Dyka, F. M., Hecker, M., and Stülke, J. (2001) Transcription of glycolytic genes and operons in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for the presence of multiple levels of control of the gapA operon. Mol Microbiol 41, 409-422.PubMed
- Prasad and Freese (1974) Cell lysis of Bacillus subtilis caused by intracellular accumulation of glucose-1-phosphate. J. Bacteriol. 118:1111-1122. PubMed
- Stülke, J., Martin-Verstraete, I., Glaser, P. & Rapoport, G. (2001) Characterization of glucose repression resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis: identification of the glcR gene. Arch. Microbiol. 175: 441-449. PubMed
- Macek et al. (2007) The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Mol Cell Proteomics 6(4): 697-707. PubMed