FbaA
- Description: fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase, glycolytic/ gluconeogenic enzyme
| Gene name | fbaA |
| Synonyms | fba, fba1, tsr |
| Essential | no |
| Product | fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase |
| Function | enzyme in glycolysis/ gluconeogenesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: fbaA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: fbaA | |
| MW, pI | 30,2 kDa, 5.03 |
| Gene length, protein length | 855 bp, 285 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | ywjH, spo0F |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 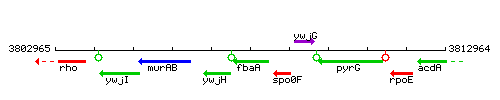
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed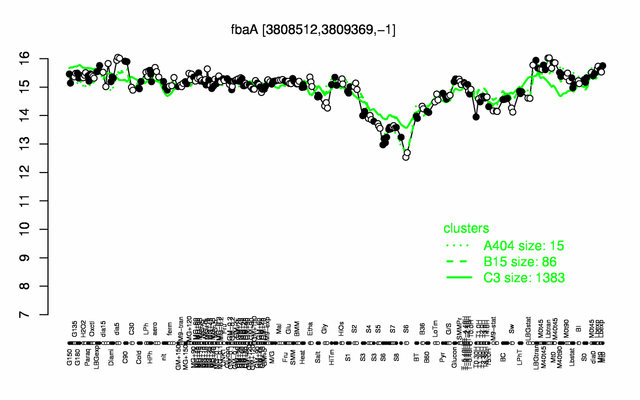
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
carbon core metabolism, phosphoproteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU37120
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU37120
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate = glycerone phosphate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: class II fructose-bisphosphate aldolase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): FbaB
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- 2 x Dihydroxyacetone phosphate binding domain (210–212), (231–234)
- Modification: phosphorylation on Thr-212 and Thr-234 PubMed
- Cofactors: Zn2+ (Metalloenzyme)
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU37120
- Structure: 3Q94 (from Bacillus anthracis)
- UniProt: P13243
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 4.1.2.13
Additional information
- Binds 2 zinc ions per subunit. One is catalytic and the other provides a structural contribution
- extensive information on the structure and enzymatic properties of FbaA can be found at Proteopedia
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- The mRNA has a long 5' leader region. This may indicate RNA-based regulation PubMed
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP591 (fbaA::cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab, PubMed
- GP596 (fbaA::erm), available in Jörg Stülke's lab, PubMed
- Expression vector:
- for expression in B. subtilis, in pBQ200: pGP1423, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- for expression/ purification from B. subtilis with N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, in pGP380: pGP88, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- for expression/ purification from E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP395, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion: pGP601 (in pAC6)
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Michael Kohlstedt, Praveen K Sappa, Hanna Meyer, Sandra Maaß, Adrienne Zaprasis, Tamara Hoffmann, Judith Becker, Leif Steil, Michael Hecker, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Michael Lalk, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Stülke, Erhard Bremer, Uwe Völker, Christoph Wittmann
Adaptation of Bacillus subtilis carbon core metabolism to simultaneous nutrient limitation and osmotic challenge: a multi-omics perspective.
Environ Microbiol: 2014, 16(6);1898-917
[PubMed:24571712]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Nico Pietack, Jörg Stülke
Essential genes in Bacillus subtilis: a re-evaluation after ten years.
Mol Biosyst: 2013, 9(6);1068-75
[PubMed:23420519]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Imke G de Jong, Jan-Willem Veening, Oscar P Kuipers
Single cell analysis of gene expression patterns during carbon starvation in Bacillus subtilis reveals large phenotypic variation.
Environ Microbiol: 2012, 14(12);3110-21
[PubMed:23033921]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Irnov Irnov, Cynthia M Sharma, Jörg Vogel, Wade C Winkler
Identification of regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(19);6637-51
[PubMed:20525796]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris Macek, Ivan Mijakovic, Jesper V Olsen, Florian Gnad, Chanchal Kumar, Peter R Jensen, Matthias Mann
The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2007, 6(4);697-707
[PubMed:17218307]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jun Hyuck Lee, Jungdon Bae, Dooil Kim, Yongseok Choi, Young Jun Im, Sukhoon Koh, Joong Su Kim, Mun-Kyoung Kim, Gil Bu Kang, Suk-In Hong, Dae-Sil Lee, Soo Hyun Eom
Stereoselectivity of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase in Thermus caldophilus.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun: 2006, 347(3);616-25
[PubMed:16843441]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Matthieu Fonvielle, Philippe Weber, Kasia Dabkowska, Michel Therisod
New highly selective inhibitors of class II fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolases.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett: 2004, 14(11);2923-6
[PubMed:15125960]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Ludwig, G Homuth, M Schmalisch, F M Dyka, M Hecker, J Stülke
Transcription of glycolytic genes and operons in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for the presence of multiple levels of control of the gapA operon.
Mol Microbiol: 2001, 41(2);409-22
[PubMed:11489127]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Ujita
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolases from spores and vegetative cells of Bacillus subtilis PCI 219.
J Biochem: 1978, 83(2);493-502
[PubMed:24624]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)