DltB
- Description: D-alanine transfer from Dcp to undecaprenol-phosphate, alanylation of teichoic acid provides some resistance against positively charged antimicrobial peptides
| Gene name | dltB |
| Synonyms | ipa-4r |
| Essential | no |
| Product | D-alanine transfer from Dcp to undecaprenol-phosphate |
| Function | biosynthesis of teichoic acid
acid (D-alanyl transfer from Dcp to undecaprenol-phosphate) |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: dltB
acid (D-alanyl transfer from Dcp to undecaprenol-phosphate) | |
| MW, pI | 46 kDa, 9.944 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1185 bp, 395 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | dltA, dltC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 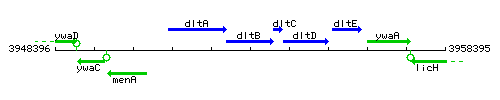
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, transporters/ other, biosynthesis of cell wall components, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
SigD regulon, SigM regulon, SigX regulon, Spo0A regulon, stringent response, YvrHb regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU38510
Phenotypes of a mutant
- more sensitive to nisin PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: membrane-bound acyltransferase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- membrane associated PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39580
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Anthony W Kingston, Xiaojie Liao, John D Helmann
Contributions of the σ(W) , σ(M) and σ(X) regulons to the lantibiotic resistome of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2013, 90(3);502-18
[PubMed:23980836]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Veronica Guariglia-Oropeza, John D Helmann
Bacillus subtilis σ(V) confers lysozyme resistance by activation of two cell wall modification pathways, peptidoglycan O-acetylation and D-alanylation of teichoic acids.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(22);6223-32
[PubMed:21926231]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Theresa D Ho, Jessica L Hastie, Peter J Intile, Craig D Ellermeier
The Bacillus subtilis extracytoplasmic function σ factor σ(V) is induced by lysozyme and provides resistance to lysozyme.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(22);6215-22
[PubMed:21856855]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Min Cao, John D Helmann
The Bacillus subtilis extracytoplasmic-function sigmaX factor regulates modification of the cell envelope and resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(4);1136-46
[PubMed:14762009]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Stephenson, C L Jensen, S T Jørgensen, C R Harwood
Simultaneous inactivation of the wprA and dltB genes of Bacillus subtilis reduces the yield of alpha-amylase.
Lett Appl Microbiol: 2002, 34(6);394-7
[PubMed:12028417]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Perego, P Glaser, A Minutello, M A Strauch, K Leopold, W Fischer
Incorporation of D-alanine into lipoteichoic acid and wall teichoic acid in Bacillus subtilis. Identification of genes and regulation.
J Biol Chem: 1995, 270(26);15598-606
[PubMed:7797557]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)