CwlO
- Description: D,L-endopeptidase-type autolysin, primary autolytic pathway for cell elongation
| Gene name | cwlO |
| Synonyms | yzkA, yvcE |
| Essential | no |
| Product | endopeptidase-type autolysin |
| Function | cell wall synthesis, cell elongation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: cwlO | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: CwlO | |
| MW, pI | 50 kDa, 5.326 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1419 bp, 473 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | trxB, yvcD |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 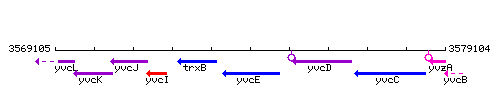
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, cell wall degradation/ turnover
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU34800
Phenotypes of a mutant
- a cwlO lytE mutant is not viable PubMed
- shorter, fatter cells, this can be rescued by addition of Mg(2+) PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: peptidase C40 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): the C-terminal D,L-endopeptidase domains of LytE, LytF, CwlS, and CwlO exhibit strong sequence similarity
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P40767
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Waldemar Vollmer
Bacterial growth does require peptidoglycan hydrolases.
Mol Microbiol: 2012, 86(5);1031-5
[PubMed:23066944]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications