FeuA
- Description: ABC transporter for the siderophores Fe-enterobactin and Fe-bacillibactin (binding protein), with YusV as ATPase
| Gene name | feuA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | ABC transporter for the siderophores Fe-enterobactin and Fe-bacillibactin (binding protein) |
| Function | acquisition of iron |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: feuA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: FeuA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Stress, Metal ion homeostasis | |
| MW, pI | 34 kDa, 8.018 |
| Gene length, protein length | 951 bp, 317 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | feuB, btr |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 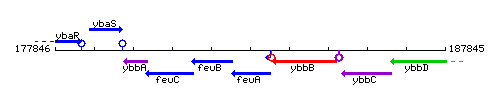
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
ABC transporters, acquisition of iron, iron metabolism, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
Btr regulon, CitB regulon, Fur regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU01630
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/biological activity:
Substrate binding protein for the triscatecholate siderophores ferri-bacillibactin and ferri-enterobactin and part of the FeuA-FeuB-FeuC-YusV ATP-binding cassette-type transporter. Furthermore ferric complexes of L-norepinephrine are bound by this protein.
- Protein family: Fe/B12 periplasmic-binding domain (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
Two independent non-symmetric globular domains, connected by a long alpha-helix (residues 143-164 of the mature protein).
- Modification:
- FeuA is a lipoprotein with a N-acetyl-S-diacyl-glyceryl-cysteine structure PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure: 2PHZ, 2WI8, 2WHY (complex with ferri-bacillibactin), 2XUZ (complex with ferri-enterobactin), 2XV1 (complex with ferric mecam)
- UniProt: P40409
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Kenji Kurokawa, Kyoung-Hwa Ryu, Rie Ichikawa, Akiko Masuda, Min-Su Kim, Hanna Lee, Jun-Ho Chae, Takashi Shimizu, Tatsuya Saitoh, Koichi Kuwano, Shizuo Akira, Naoshi Dohmae, Hiroshi Nakayama, Bok Luel Lee
Novel bacterial lipoprotein structures conserved in low-GC content gram-positive bacteria are recognized by Toll-like receptor 2.
J Biol Chem: 2012, 287(16);13170-81
[PubMed:22303020]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Marcus Miethke, Arne Skerra
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin expresses antimicrobial activity by interfering with L-norepinephrine-mediated bacterial iron acquisition.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother: 2010, 54(4);1580-9
[PubMed:20086155]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Florian Peuckert, Marcus Miethke, Alexander G Albrecht, Lars-Oliver Essen, Mohamed A Marahiel
Structural basis and stereochemistry of triscatecholate siderophore binding by FeuA.
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl: 2009, 48(42);7924-7
[PubMed:19746494]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Rebecca J Abergel, Anna M Zawadzka, Trisha M Hoette, Kenneth N Raymond
Enzymatic hydrolysis of trilactone siderophores: where chiral recognition occurs in enterobactin and bacillibactin iron transport.
J Am Chem Soc: 2009, 131(35);12682-92
[PubMed:19673474]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Birgit Voigt, Haike Antelmann, Dirk Albrecht, Armin Ehrenreich, Karl-Heinz Maurer, Stefan Evers, Gerhard Gottschalk, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Thomas Schweder, Michael Hecker
Cell physiology and protein secretion of Bacillus licheniformis compared to Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2009, 16(1-2);53-68
[PubMed:18957862]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ahmed Gaballa, John D Helmann
Substrate induction of siderophore transport in Bacillus subtilis mediated by a novel one-component regulator.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 66(1);164-73
[PubMed:17725565]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Marcus Miethke, Oliver Klotz, Uwe Linne, Jürgen J May, Carsten L Beckering, Mohamed A Marahiel
Ferri-bacillibactin uptake and hydrolysis in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 61(6);1413-27
[PubMed:16889643]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Juliane Ollinger, Kyung-Bok Song, Haike Antelmann, Michael Hecker, John D Helmann
Role of the Fur regulon in iron transport in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(10);3664-73
[PubMed:16672620]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Mayuree Fuangthong, John D Helmann
Recognition of DNA by three ferric uptake regulator (Fur) homologs in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(21);6348-57
[PubMed:14563870]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Noel Baichoo, Tao Wang, Rick Ye, John D Helmann
Global analysis of the Bacillus subtilis Fur regulon and the iron starvation stimulon.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 45(6);1613-29
[PubMed:12354229]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Quentin, G Fichant, F Denizot
Inventory, assembly and analysis of Bacillus subtilis ABC transport systems.
J Mol Biol: 1999, 287(3);467-84
[PubMed:10092453]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)