MurG
- Description: UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-N-acetylmuramyl-(pentapeptide)pyrophosphoryl-undecaprenol N-acetylglucosamine transferase
| Gene name | murG |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-
N-acetylmuramyl-(pentapeptide)pyrophosphoryl-undecaprenol N-acetylglucosamine transferase |
| Function | peptidoglycan precursor biosynthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: murG | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Cell wall | |
| MW, pI | 39 kDa, 9.568 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1089 bp, 363 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | spoVE, murB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA Advanced_DNA |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed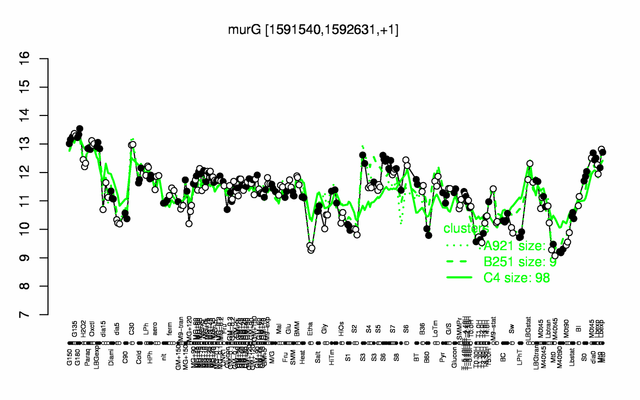
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, biosynthesis of cell wall components, sporulation proteins, essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15220
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: UDP-N-acetylglucosamine + Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)-diphosphoundecaprenol = UDP + GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)-diphosphoundecaprenol (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: MurG subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- UniProt: P37585
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.4.1.227
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Katarína Muchová, Anthony J Wilkinson, Imrich Barák
Changes of lipid domains in Bacillus subtilis cells with disrupted cell wall peptidoglycan.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 2011, 325(1);92-8
[PubMed:22092867]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Warawan Eiamphungporn, John D Helmann
The Bacillus subtilis sigma(M) regulon and its contribution to cell envelope stress responses.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 67(4);830-48
[PubMed:18179421]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ahmed Bouhss, Amy E Trunkfield, Timothy D H Bugg, Dominique Mengin-Lecreulx
The biosynthesis of peptidoglycan lipid-linked intermediates.
FEMS Microbiol Rev: 2008, 32(2);208-33
[PubMed:18081839]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jean van Heijenoort
Lipid intermediates in the biosynthesis of bacterial peptidoglycan.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2007, 71(4);620-35
[PubMed:18063720]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Patrick Eichenberger, Masaya Fujita, Shane T Jensen, Erin M Conlon, David Z Rudner, Stephanie T Wang, Caitlin Ferguson, Koki Haga, Tsutomu Sato, Jun S Liu, Richard Losick
The program of gene transcription for a single differentiating cell type during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
PLoS Biol: 2004, 2(10);e328
[PubMed:15383836]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
A A Branstrom, S Midha, C B Longley, K Han, E R Baizman, H R Axelrod
Assay for identification of inhibitors for bacterial MraY translocase or MurG transferase.
Anal Biochem: 2000, 280(2);315-9
[PubMed:10790316]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Theeragool, A Miyao, K Yamada, T Sato, Y Kobayashi
In vivo expression of the Bacillus subtilis spoVE gene.
J Bacteriol: 1993, 175(13);4071-80
[PubMed:8320223]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A O Henriques, H de Lencastre, P J Piggot
A Bacillus subtilis morphogene cluster that includes spoVE is homologous to the mra region of Escherichia coli.
Biochimie: 1992, 74(7-8);735-48
[PubMed:1391053]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)